Simply put, SOP are guidelines related to procedures that must be carried out. For example, in a company, company SOP are all the guidelines that employees need to do to get good work results.
This rule itself is not only about how to get the job done. There are SOP if there is a disaster, SOP if employees are allowed to work, SOP if employees are about to change jobs, and so on.
In essence, this SOP will arrange for everything to run properly, correctly, and effectively.
Definition of SOP
Simply put, as previously explained, SOP are a series of procedures that need to be carried out to get the desired results. Later, this will be a guide for employees on what they should do.
Meanwhile, there are some experts who also have an opinion about the meaning of SOP itself. SOP are guidelines used to ensure the operational activities of a company or organization run smoothly.
SOP is a sequence of steps in terms of implementing work, where the work is carried out. It deals with what to do, how to do it, when and where to do it, and who should do it.
SOP is a document that contains a series of written instructions. The document is standard and official.
The document contains a series of processes for administering office administration which contains how to do the work, the time of execution, the place of implementation, and also who will carry it out.
SOP function
In its own making, SOP have several functions. At least this company SOP is a work guideline that must be obeyed by all parties.
Try to imagine if a company does not have an SOP. So, every time there is a new employee, the employee will be confused about what they should do.
The employee will also be confused about his duties, rights, and responsibilities. This is one of the functions of the existence of this standard rule.
The existing SOP will be a guide for each employee to carry out their duties. Likewise, when there are new employees, the old employees do not have to bother explaining a lot of things about work culture.
Old employees only need to explain certain things.
In addition, this rule also has several other functions, such as:
1. As a Work Guide
SOP will serve as a guide when working. With this rule, it will be easier in terms of operations .
This guide will contain the steps in doing the job. This will be very useful to assist employees in carrying out and completing their duties.
This will also help improve the performance of the company. That’s because every job will be purposeful.
In this case, employees will know what they need to do, what their rights and responsibilities are, what work standards the company expects, and the limits of their work.
Furthermore, this rule will help the company to achieve its goals. And on the other hand, by applying this rule properly, the company will also help employees to work optimally.
2. As a Legal Basis
SOP will also serve as a legal basis. This will relate to the rights and responsibilities of each party.
If later there is one party who violates this rule, then the punishment that that party will get is usually already stated in the rule.
By adhering to this guide, it will also be easier for each error to find the cause.
This is because it is enough to see which parties are working not in accordance with the existing SOP.
3. Providing Job-Related Information
In its application, company SOP are all rules or stages that will be related to work. Later, this company guideline is not only about procedures, but will also contain all the possibilities that occur while working.
This includes possible problems and obstacles that will arise during work .
The SOP will manage all the steps when this happens. In other respects, this guide will also set out what all parties need to do, in the event of a natural disaster, for example.
4. Work Discipline Guidelines
The essence of the contents of the SOP is the rules that need to be followed by all parties. This rule also contains the consequences they will get if they violate.
With this, another benefit of the company’s SOP is to create work discipline.
Purpose of SOP
From the benefits obtained by the existence of SOP, these rules also have a purpose in making them. Some of these goals include:
1. Minimizing Errors
With the SOP in effect, it is hoped that every party present will follow it and understand what they need to do.
Later, this will be one way to minimize errors.
2. Employees Find Out More About Their Jobs
Regarding how to reduce errors. This is partly because every employee will understand what they need to do.
This in addition to minimizing errors can also be a way to improve the performance of employees.
3. New Employees Will Easily Adapt
With this guide, every new employee will be able to immediately know what their rights and responsibilities are. They will also find it easier to know about the details of the work they need to do.
4. Helping the Company Reach the Target
With the SOP, one of the goals is to help companies achieve the targets they set. This guide will contain guidance on how to work effectively and efficiently.
This will be one way to help the company achieve its targets.
SOP Benefits
SOP itself is one thing that companies must have. In this case because these guides and guidelines themselves have many benefits.
The main benefit is of course to provide written guidance on what employees should do. In addition, other benefits of company SOP are :
1. Increase Reputation
SOP is one of the characteristics of the company’s seriousness in running a business. In the client’s eyes, companies that have clear rules are considered to know what they are doing and how to do it.
In this case, one of the benefits of SOP is to increase the reputation or good name of the company itself. When the company runs the existing rules well, the client’s assessment will be good.
2. SOP are Guidelines for Working
A company certainly does not want its employees confused about what they should do. This is one of the benefits of having SOP.
With this guide, it will really help employees to work according to their respective duties and obligations. This will make the work more effective and also avoid overlapping tasks or escaping responsibilities.
Furthermore, the guide will also make the finished work standard.
3. SOP is a system that will make it easier
In connection with the previous point, the SOP will also be a system that will simplify the work in many ways. For example, if an error occurs, then the process of tracing the error will be easy.
With this guide, all parties involved will know what they have to do, what the standards are, and to what extent.
4. Maintaining the Company’s Characteristics
Another benefit of implementing SOP is that they can maintain the company’s characteristics. Company SOP are guidelines that all employees must follow.
With this guide, whoever does the work will produce a product of the same quality and standard.
This is because each employee will not work forever. So, with the company’s SOP, it is hoped that when there is a change of employees, it will not affect the quality of production.
5. Provide Clear Rules
With the SOP, this indirectly also becomes a rule that all parties must follow. Everyone associated with the guidelines must make it a rule.
Later, in the guidelines themselves, there will be rules regarding parties who do not follow these guidelines and guidelines properly.
For example, in a company there are rules that require all employees to wear uniforms.
When there are employees who do not wear uniforms, the SOP rules will also regulate what punishments the employee will get. In this case, this guide will also be useful as a provider of clear rules.
Tips for Making SOP
In every SOP preparation there are at least a few things that need to be considered. One of them is a matter of principle in the formulation of the rules themselves.
Principles in Preparing SOP
Because of its very important function, the making of the SOP itself cannot be made haphazardly.
At least, in its manufacture there are several principles that need to be considered. Some of these principles include:
1. Clear and Easy to Understand
Because it will be a guideline and many people will use it, every rule and step in the SOP must be clear and easy to understand.
In its application, each step in this guide must contain a detailed description so that it is easy to implement.
In addition, the making of this guide should also use simple and uncomplicated language.
This is to avoid misunderstandings when interpreting the meaning in the guide itself.
2. Effective and Efficient
One of the goals of making SOP is that all parties will easily understand what they have to do. That is why, in making this rule, it must be able to make all work systems effective and efficient.
Every work procedure in the SOP must be made efficiently. This is to maintain the efficiency of time, energy, and of course costs.
However, this efficiency will also be closely related to effectiveness. In this case, the company’s target must be the highest benchmark.
Simply put, in its manufacture, the company’s SOP must be made based on the company’s own goals. This rule will be a way to realize these goals in an efficient and effective manner.
3. Alignment
Another principle in the preparation of SOP is harmony. One of these alignments relates to the goals of the company.
In addition, this alignment is also related to the vision, mission, resources, and also several other things.
4. Dynamic
In this case, the SOP can change at any time. Of course these changes occur with prior notice.
Changes in the rules are important because they must adapt to existing conditions.
This is where the importance of evaluating the SOP itself. Later, any existing deficiencies can be corrected and produce new, better rules or guidelines.
5. Measurable
One of the goals of making SOP is to help companies achieve their goals or targets. In this case, it is this goal or target that must be measurable, both in quantity and quality.
The measurable principle in making this rule is also important, one of which is as an evaluation material. With a clear measure, it will be easy to judge whether the existing rules are still relevant or not.
6. Open
One other principle that needs to be considered when making SOP is openness. That means every rule must be transparent .
Each party must know clearly all rights and responsibilities.
This openness also means that every rule is subject to change. When the applicable rules are deemed ineffective or no longer relevant, changes can be made.
7. Legal certainty
In addition to work procedure problems, SOP will also usually regulate if an error occurs. In this case, it will also contain punishment.
Every punishment that exists must of course be in accordance with applicable law.
The SOP will also regulate if one of the parties does not follow the applicable guidelines. Furthermore, the guidelines also regulate whether an employee can be protected or not if he or she is subject to a lawsuit.
Tips for Preparing SOP
In addition to paying attention to the principles as above, in making SOP there are also some tips that can be one way to make effective and good rules.
Some tips for compiling these rules include:
1. Determining the Right Person
You probably already understand how important an SOP is for the company. That is why the manufacturing process cannot be arbitrary.
Therefore, the person or team that composes this rule cannot be an arbitrary person.
In this case, besides needing people who have writing skills, making SOP also requires people who understand the technical and non-technical matters of the company.
In some cases, company SOP are also prepared by external parties they hire.
2. Create Interesting Visuals
The SOP will contain many guidelines that will serve as guidelines for many people. This will cause problems if the existing guide is only available in text or written format.
This is because some people actually understand better when they see pictures.
In addition, the visual function of the SOP is to make people interested in reading it. A guide that contains lots of rules and guidelines will be very boring if it’s just text or text.
3. Pay attention to the writing style
In this case, always pay attention to who your target is. The mistake that often occurs is that the SOP is made with writing or language style that is not in accordance with the target.
Even though they have the same goals and objectives, the guide for the engineering section cannot be the same as the guide for the finance section. This is because the understanding of each person will be different.
If this happens, it will only cause confusion in the translation of the guide itself.
To avoid this, it is better when making SOP each division or section participates. This is useful for equalizing understanding and also creating more detailed guidelines.
4. Pay Attention to Work in the Field
In this case, every SOP making must pay attention to who will use it and also how it will be implemented later.
Also make sure if you use it later it doesn’t cause other problems.
That is the importance of paying attention to any existing guidelines. That way, when you create a new guide, you can learn what is missing. To be repaired later.
5. Do Testing Before SOP Launch
It’s a good idea, before the SOP becomes a fixed rule, do a test for a certain time. This is useful for assessing whether the new rules have met expectations or not.
In addition, this test will also assess how the response from employees or related parties. Like, whether this new rule makes it easier or makes it more complicated.
6. Make Sure Every Rule Has A Reason
In each rule will definitely raise questions about why you made the rule. Here, then you need to provide answers to these questions. Give a reasonable reason why the rule exists.
Don’t let anyone think that the rules are made only to benefit the other party.
7. Make Sure All Parties Agree
Since the implementation of this SOP will be a shared responsibility, it is also quite important to ensure that all parties involved agree on the rules. This agreement is also to avoid the emergence of conflicts in the future.
8. Always Review Existing SOP
The current rules are an improvement over the previous rules. It also confirms that the current rules are still subject to change.
This could be because the rules are no longer relevant, conditions have changed, or other factors.
This is where it is important to always monitor any applicable rules. If it is felt that there are many shortcomings, then the rules can be immediately changed.
Of course, each of these changes must also be known by all parties.
SOP Example
In its use, of course the SOP of each company will be different. This will depend on the prevailing work culture in the company.
However, in essence, each of these rules will have the same goal.
Here are some examples of SOP that you can learn:
Example of Company SOP on Computer and Internet Use
|
Title |
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE FOR USE OF COMPUTER AND INTERNET |
| 1 |
Background |
1. Each employee is given a computer which is the office inventory |
|
|
2. Every computer is connected to the internet provided by the office |
|
|
3. Control the use and utilization of computers and the internet in the work environment during working hours. |
| 2 |
Destination |
1. Optimizing the use of computers and internet for office facilities for work purposes. |
|
|
2. Use of computer and internet office facilities for the right things. |
| 3 |
Scope |
Use of computers and internet for each employee |
| 4 |
Responsibility |
1. IT Department |
|
|
2. Spv of each section |
|
|
3. Every employee |
| 5 |
Work Units Involved |
1. IT Department |
|
|
2. Internal Audit |
| 6 |
Implementation Procedure |
1. Every employee uses the office computer and internet only for work purposes and not for other purposes outside of work. |
|
|
2. Each employee is responsible for the office inventory computer that each uses. |
|
|
3. File storage on each computer is arranged as neatly as possible. Use clear folder names. |
|
|
4. Perform anti-virus scans periodically. Use an anti-virus that is already available |
|
|
5. If there is any discrepancy or damage during use, immediately contact the IT Department. |
|
|
6. If you feel the need to improve the quality of the device, then carry out the submission procedure with the knowledge of the IT Department |
| 7 |
Recording |
Internal memo to each division. |
Furthermore, each SOP will be signed by the maker, examiner, and those who approve.
After the SOP is published, it will become the applicable guidelines and rules.
Sample Company SOP on Uniforms
In addition to the format as before, usually this rule will also be spread in a simpler format. Usually in this format, the information provided is only about the implementation procedure.
Usually this is the format that employees see most often. Here is an example:
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE
About: Uniform Use
- Every employee is required to wear the official uniform that has been determined.
- Every employee is required to use an ID Card while in the work environment.
- Each employee may only wear black or dark colored shoes.
- Every employee is prohibited from using excessive accessories during work.
That’s an example of a Standard Operating Procedure for uniform use. Rules with this format are usually the ones that will be distributed and pasted in places that are easily read by many people.
In the rules, this format usually only contains the signature of the maker or person in charge of the rule.
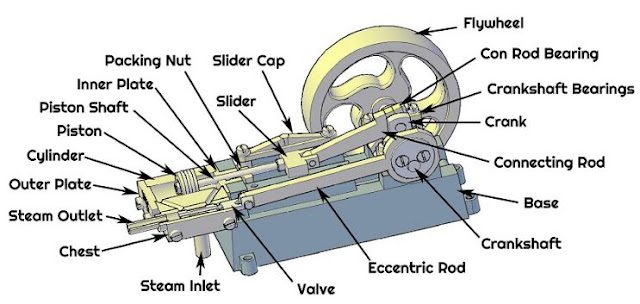
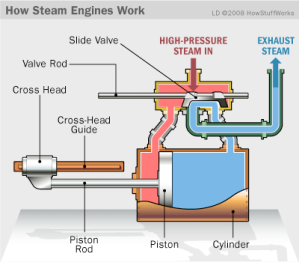
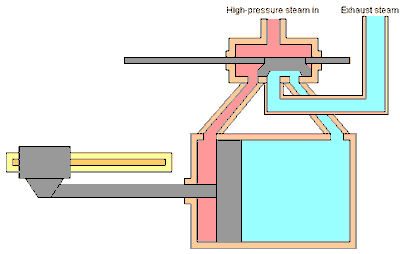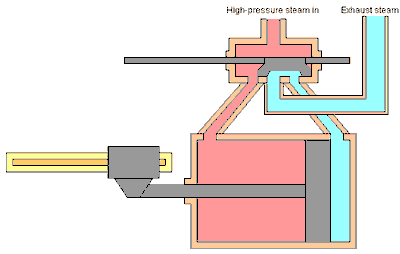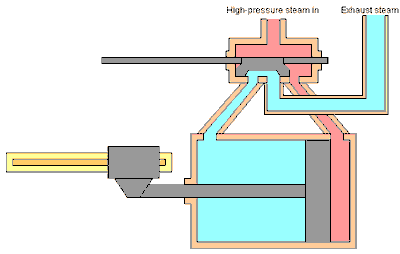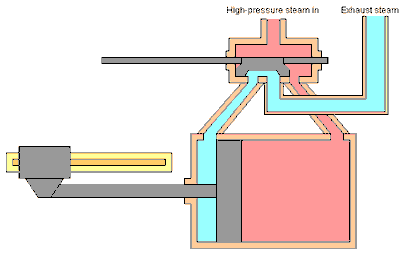
In addition to the format as above, there are several other formats of making this rule. For example, using images.
Usually this is for guidance on technical matters. By using images, the hope is that users will become easier to understand.
In addition, the current guide format also uses audio-visual media. This is to make distributing this guide easier.
In addition, this format is also considered more effective, because in addition to hearing and seeing directly, users can also choose to see only or only hear.
In addition to making it more interesting, some places also make this SOP format in the form of animation. Although the format is different, but the purpose of making this guide remains the same.
Its main goal is to make it easier for users to do what they need to do. This guideline is also useful for providing clear boundaries.
If it is associated with company SOP, then the goal is that each party or division knows what their duties, responsibilities and rights are. Later, this will be the basis and benchmark in each of their work.
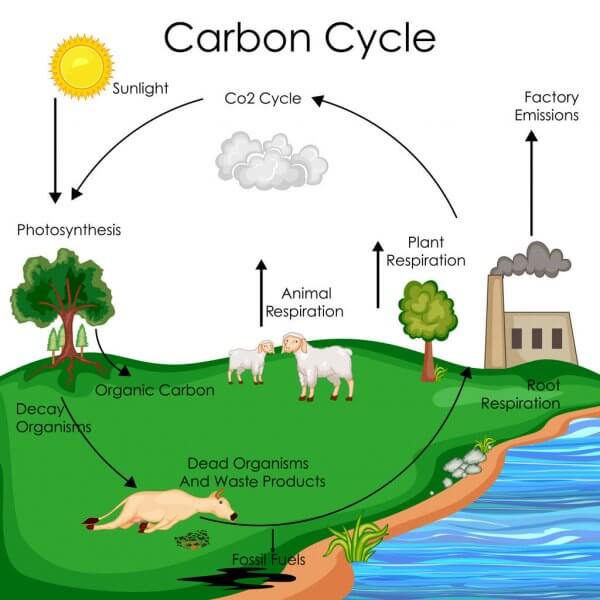
SOP can also be a reference standard for any existing work. In addition, SOP will also be very useful to inform all parties about what they should do when something happens such as a natural disaster or fire.







































![Discussion of the Photosynthesis Process in Plants [+Image]](https://sinaumedia.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/Photosynthetic-Process.jpg)