In this article, you will learn what the components of a steam engine are and how they work. Steam engine is a technology that converts heat energy into motion energy. The steam engine has a way of working using physical concepts that apply the laws of thermodynamics.
Inventor of the Steam Engine
We know James Watt as the inventor of the steam engine in the mid-18th century. In that year, the invention of the steam engine became one of the most revolutionary inventions in history because it revolutionized the industrial world. The invention of the steam engine was the beginning of the industrial revolution.
But in fact, James Watt was not the first inventor. James Watt made repairs to the previous steam engine on the condenser and shaft parts.
So who invented the steam engine? So the answer to the inventor of the steam engine is Thomas Newcomen. The steam engine invented by Thomas Newcomen in 1712 had the purpose of pumping water in the mining world. While James Watt made repairs in 1776.
After improvements by James Watt, the steam engine operated more efficiently and moved more smoothly in its energy conversion process. Through its improvements, the steam engine can be applied in industry more efficiently.
James Watt worked with Matthew Boulton to design steam engines for industries in Europe.
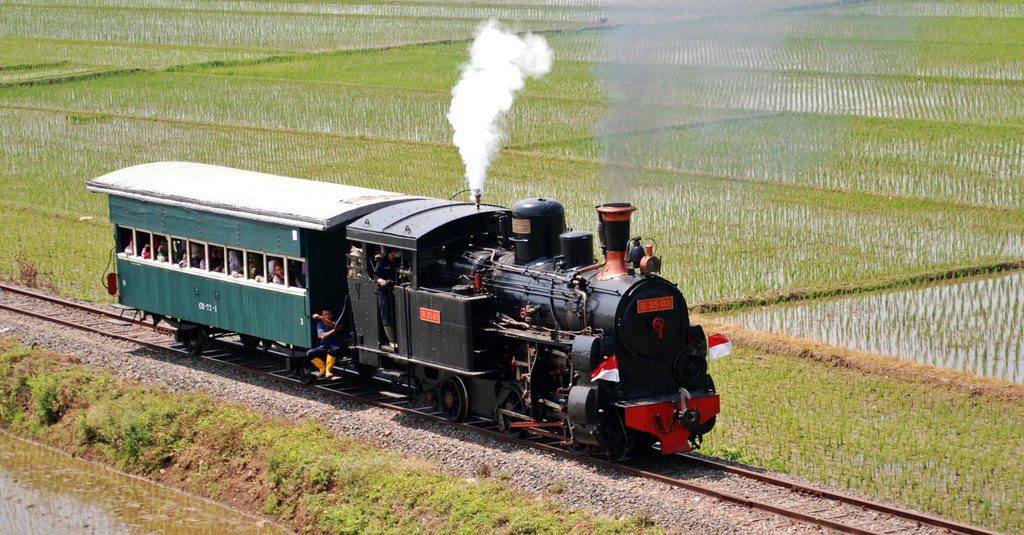
Not only for industry, the use of steam engines is increasingly developing as a means of supporting land transportation. Steam engines began to replace animal power during the industrial revolution, one of which was the steam locomotive. Animal power began to be replaced by steam engines in 1830 when there was a race between horses and steam engines.
In the early 19th century, the steam engine underwent continuous improvement until it became more efficient with a smaller size.
Steam Engine Components
The working principle of a steam engine can occur because the components are interconnected into a system. The components of a steam engine consist of frames, pistons, cylinders, bearings, valves, etc.
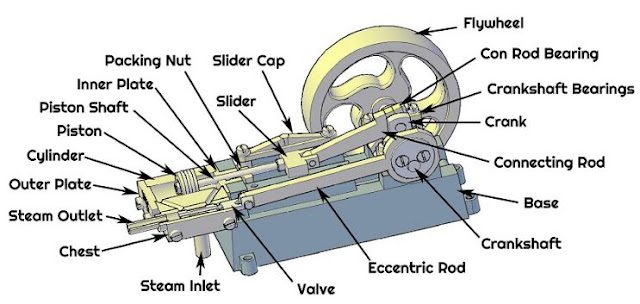
1) Frame
Steam engine has a frame or frame that has a function as a container to connect the components in it. A steam engine frame is made of metal casting material because it is more resistant to thermal expansion.
2) Cylinder
Component Cylinder or cylinder on a steam engine is a part or component in the form of a room that has a function to accommodate steam and piston movement. Some engineers refer to the cylinder on a steam engine as the crankcase.
3) Steam Chest
Steam Chest on a steam engine is a part or component of a steam engine that is integrated with the cylinder. This Steam Chest generally has a cube or spherical shape depending on the valve used.
4) Main Bearings
Bearing is a component or part of a steam engine that has a function to maintain the rotating axis of a shaft. Because friction or flexion often occurs, the inner bearing surface needs to be coated with lubricant.
5) Piston
piston in the steam engine has a similar way of working like the piston in a car engine or motorcycle engine in general. The piston in the steam engine has a function to continue the steam compression force into rotation.
6) Piston Rings or Piston Rings
A piston has rings to keep steam from penetrating between the pistons and cylinders.
7) Piston Rod or Piston Rod The piston
rod in a steam engine has a function to transmit the compressive force on the piston head to a rotary crank.
8) Stuffing Box
The Stuffing Box on the steam engine has a function as a seal to prevent the steam in the system from escaping into the atmosphere. If a leak occurs, the energy in the steam engine system will not be maximized.
9) Crosshead
Crosshead on a steam engine has a function so that the movement of the piston is not sideways and out of line.
10) Connecting Rod or Piston
Rod Connecting Rod on a steam engine has a function to connect the piston to the crankshaft.
11) Valve / Valve
As previously explained that the valve is a part of the cylinder and steam chest. The valve on the steam engine has a function as a gate for the entry and exit of steam in the system.
12) Valve Rod and Eccentric Rod
Eccentric Rod The machine has a slab-like shape that has the function of converting rotary motion into linear motion. Why do we need linear motion in steam engines? The answer is to open and close the valve.
13) Flywheel
Free Will or we call it the gear on a steam engine is a mechanism to dampen the rotation suddenly. So that the torque on the steam engine becomes more stable.
How Does Steam Engine Work?
Steam engines are included in the category of heat engines, namely equipment used to convert thermal energy from fuel into mechanical energy through the combustion process. There are two types of heat engines, namely Internal Combustion Engines (ICE) and External Combustion Engines (ECE). In ICE-type heat engines, the process of burning fuel to produce mechanical power is carried out within the equipment itself; while in ECE, this equipment only converts thermal energy into mechanical energy while the combustion process is carried out outside the equipment.
Examples of ICE-type heat engines are gasoline and diesel engines, which are very popular as prime movers for both automotive and industrial use. In gasoline and diesel motors, the process of burning fuel (gasoline/diesel) is carried out in the motor cylinder itself and the change in thermal energy resulting from combustion into mechanical energy is also carried out in the aircraft itself through the back and forth movement of the piston into rotational movement of the crank shaft.
Examples of ECE-type heat engines are steam engines and steam turbines. In this equipment, the steam engine only converts the potential energy of the steam into mechanical energy in the form of to and fro movement of the piston and then converted into rotational motion of the crank shaft; while the steam turbine converts the potential energy of the steam into mechanical energy which is directly the rotational motion of the turbine axle. The fuel combustion process is carried out outside the steam engine and steam turbine, namely in the boiler (boiler). In the boiler (boiler) the thermal energy from the combustion of fuel is used to heat water so that it turns into steam with high temperature and pressure, then the steam with high temperature and pressure is flowed to a steam engine or steam turbine to be converted into mechanical power.
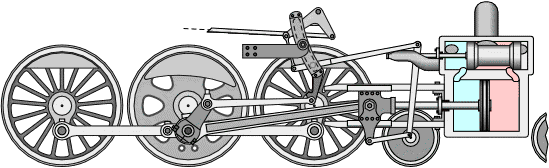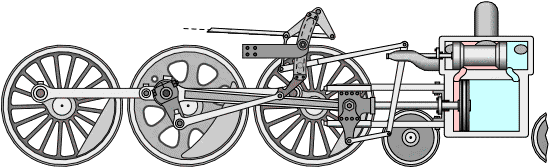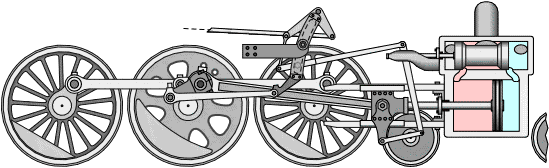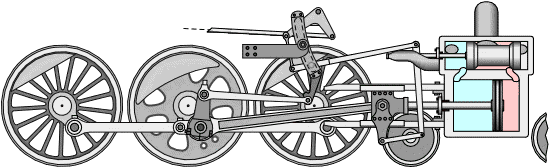
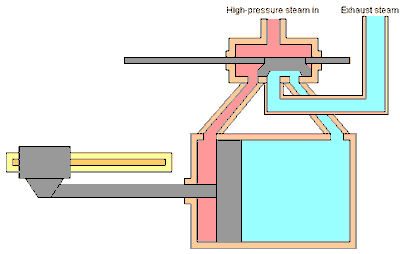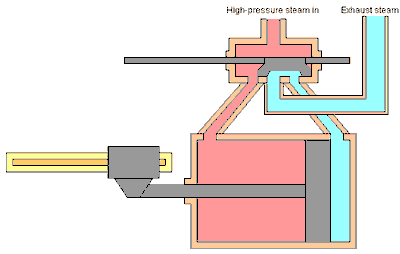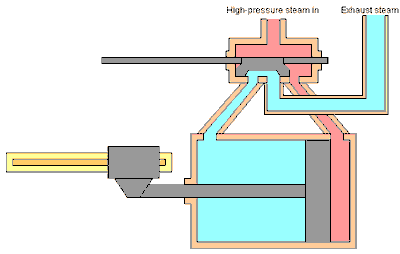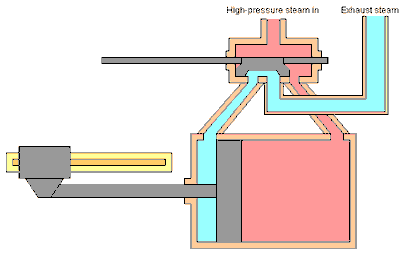
The workings of the steam engine are as follows: See the picture below,
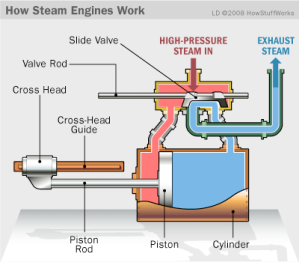
Inside the steam engine cylinder there is a piston which has a piston rod connected to a cross head which is outside the cylinder. The cross head is connected by a connecting rod to the crank shaft (not shown in the picture), so that when the piston moves to and fro, the crank shaft can rotate.
The slide valve which has a valve rod is driven by the crank shaft through an eccentric, so that the slide valve can move to and fro while opening and closing the two steam holes connected to the cylinder. The valve box where the slide valve is located has two channels, the intake channel is connected to the boiler to deliver high pressure steam (red color), and the exhaust channel is connected to the chimney to remove used steam (blue color).
When the piston reaches the leftmost position, the slide valve will open the steam hole of the left cylinder so that steam from the boiler can enter the cylinder on the left side of the piston and push the piston to the right, while the right steam hole is connected to the exhaust channel so that the used steam can be drained. discharged through the chimney. Before the end of the piston stroke, the steam hole is closed by the slide valve so that the steam supply stops but the piston continues to move to the right due to the expansion of the steam.
When the piston reaches the far right position, the slide valve will open the steam hole of the right cylinder so that steam from the boiler can enter the cylinder on the right side of the piston and push the piston to the left, meanwhile the left steam hole is connected to the exhaust channel so that used steam can be wasted. through the chimney. Before the end of the piston stroke, the steam hole is closed by the slide valve so that the steam supply stops but the piston continues to move to the right due to the expansion of the steam.
Because the cross head with the crankshaft is connected by a connecting rod, the back and forth movement of the piston will be converted into rotational motion of the crankshaft. Thus as long as there is a supply of steam from the boiler, the steam engine will turn into mechanical power with the rotational movement of the crank shaft.
Steam locomotives usually have 2 steam engines mounted on the right and left of the locomotive, the rotational motion produced by the two steam engines is directly used to turn the locomotive wheels so that they are able to pull the entire train series (see picture below).