Data Collection Techniques in Research Design – Have you ever collected data by means of interviews? This activity is the most important activity in a research. When the plan has been carefully prepared but the data collection and analysis activities are not carried out properly, the objectives that have been set are not achieved properly.
In other words, data collection and analysis activities are the implementation stage in the process of conducting research. The collection and analysis of research data is based on a method or procedure so that the desired data can be collected completely from the field. The following is an explanation of data collection techniques and research data processing. Check these out!
Definition of Data Collection Techniques
Data collection techniques are methods used to collect information or facts in the field
Data collection was carried out to obtain the information needed in order to achieve the research objectives. Before conducting research, a researcher usually has a guess based on the theory he uses, this assumption is called a hypothesis. To prove the hypothesis empirically, a researcher needs to collect data to be investigated in more depth.
The data collection process is determined by the variables in the hypothesis. Data collection is carried out on a predetermined sample. Data is something that has no meaning for the recipient and still requires processing.
Data can have various forms, ranging from images, sounds, letters, numbers, language, symbols, and even circumstances that can assist research results later.
All of these things can be called as data as long as we can use it as material to see the environment, object, event, or a concept. Data can be divided into several categories.
Types of Data According to How to Obtain It
The types of data can be categorized as follows according to how they are obtained, including:
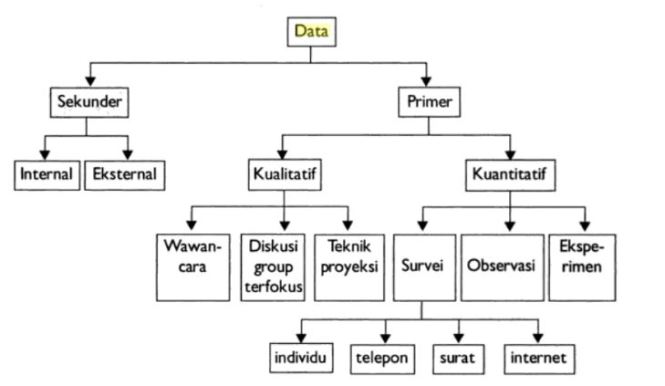
- Primary data , namely data collected and processed by the researcher himself directly from the subject or object of research.
- Secondary data , namely data obtained not directly from the object or research subject.
Types of Data by Source
The types of data can also be categorized according to the way they are sourced, including:
- Internal data , namely data that describes the state or activities in an organization
- External data , namely data that describes a situation or activity outside an organization.
Types of Data by Their Nature
The types of data can also be categorized according to their nature, including:
- Quantitative data , namely data in the form of exact numbers, which can be measured ( measurable ) or can be calculated using numeric variables or numbers
- Qualitative data , namely data that is not in the form of numbers or data from verbal word explanations so that it cannot be analyzed in the form of numbers or numbers.
Examples of quantitative data:
- Data on the total number of students each year in a school
- Data on the total sales of goods in a supermarket every day
- Visitor data of a website
- Tourist visit data for a province
Examples of qualitative data:
- Description of an area under study
- Biographies of resource persons used as research references
- The history of the establishment of a company under study
Types of Data by Time of Collection
The types of data can also be categorized according to the time of collection, including:
- Cross section / incidental , ie data collected only at a certain time
- Periodic data / time series , namely data collected from time to time to describe a development or trend of circumstances / events / activities.
The Importance of Data Collection in Research Design
Data collection is the recording of events or things or information as well as the characteristics of some or all elements of the population that will support and support research.
Data is the plural form of datum. Data is information about something, it can be something that is known or in the form of an assumption. This data can also be in the form of facts depicted through numbers, symbols, and codes.
List of Questions in the Data Collection Process
The questionnaire is an important standard data collection tool in the form of a series of questions about a number of indicators from a number of variables that are ordered in such a way as to facilitate the interview. There are several things that must be considered before making a list of questions, namely as follows:
- There is clarity of concepts and variables used
- Standardization (each respondent will be asked the same question)
- Objectivity (questions must be as neutral as possible)
- Unit Relevance (there is accuracy in the selection of units or elements of data sources with research problems)
Question Type
Judging from the type of questions posed in the list of questions can be divided into several types of questions, namely:
- Questions about facts ( e.g. questions about Age, occupation, etc.)
- Questions about Opinion, for example, what is someone’s opinion about the existence of electricity entering the village?
- Questions about information or knowledge, for example, “Since when did electricity enter this village?”
- Questions about perception (this question is a question that seeks to measure how respondents judge something in relation to other things or other people).
Data Based on the Source of Retrieval
The list of questions cannot be separated from research, especially in the data collection process. Based on the source of data collection is divided into:
- Primary Data or
data obtained or collected directly in the field by the person conducting the research or the person concerned who needs it.
Primary data is also known as original data.
- Secondary Data i.e.
data obtained or collected by people conducting research from existing sources.
This data is usually obtained from the library or from previous research reports. This secondary data is also known as available data.
Question Forms
While seen from the form, the questions can be divided into three forms, namely:
- Closed questions are questions that are equipped with a number of alternative answers. Respondents just choose one of the alternative answers. Respondents just have to choose one of the alternatives that have been provided according to their choice.
- Open-ended questions are types of questions that are not accompanied by alternative answers. So the respondent is free to express the answer according to the will of the respondent.
- A half-open question , which is a question in which a number of alternative answers are available, it is also possible for the respondent to present an answer according to his will.
Based on its nature, data can also be divided into two, namely qualitative data and quantitative data. Qualitative data is data that is not in the form of numbers, while quantitative data is data in the form of numbers.
Data Based on Level of Measurement
Based on the level of measurement, the data is divided into four, namely:
- Nominal Data is Data that comes from grouping events based on certain categories, the difference only showing qualitative differences
- Interval data is data that comes from objects or categories that are sorted by a certain effect, where the distance between each object is the same. In this data, not against absolute zero
- Ordinal data is data that comes from objects or categories arranged according to size, from the lowest level to the highest level or vice versa with distances that do not have to be the same.
- Ratio data is data that collects all the characteristics of nominal data, ordinal data, and interval data. Figures in this data, indicate the actual size of the object being measured.
Data Collection Techniques in Social Research
Social research is conducted to solve problems using the theory and knowledge that has been learned. Research is also a requirement for students before completing their studies.
Through social research, we are required to apply the material we have learned to the real world and recognize the patterns that occur in society.
When conducting research, we also need to identify the data collection techniques that need to be carried out. Data collection techniques are the methods used by researchers in obtaining data in the field. In social research, there are several techniques that are commonly used, namely:
- questionnaire,
- literature review,
- interview, and
- observation.
Questionnaire
Questionnaires or questionnaires are data collection techniques by asking questions to be answered by respondents, usually in writing.
Questionnaires are used when researchers want to know the perceptions or habits of a population based on respondents. Questionnaires that are distributed must be tested beforehand to find out if the questions entered can be used as a valid and reliable measuring tool.
In general, questionnaires are used in quantitative research analysis using SPSS or the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences which is quite complicated.
Questionnaires can be in the form of printed or online questionnaires. Literature Study The most commonly used data collection technique is literature study. Literature study collects relevant data from books, scientific articles, news, and other credible sources related to the research topic.
Advantages of the Questionnaire method
- In this technique the respondent fills in by themselves so that no interview is needed.
- In terms of cost, this technique requires a relatively low cost.
- In terms of time, this technique saves time, meaning that it can be sent to various different places at the same time, so that the return can be received in a not too long time.
- With this technique, respondents can more freely fill out the questionnaire, without feeling embarrassed because no one is interviewing.
- There was no influence from the interviewer who gave the questionnaire or questionnaire.
Weaknesses of the Questionnaire include:
- Less flexible
- Low rate of return of the questionnaire
- Unable to observe the respondent’s reaction when answering the question
- The atmosphere of the environment when the respondent filled out the questionnaire was not controllable. It is possible that the questionnaire was filled out by someone else not the respondent
- It is difficult to control respondents to answer in accordance with the order of questions in the questionnaire
- Unable to use complex questionnaire formats.
Literature review
Literature studies can strengthen the background for doing research and allow us to study previous research, so that we can produce newer research. Interviews Interviews were conducted by means of question and answer with respondents or informants to obtain information needed for research. Literature Studies can be done through:
- Editing – Editing is the process of re-examining the data that has been collected to find out whether the data is good enough and can be immediately prepared for the next process. The purpose of editing, basically, is to eliminate errors contained in the recording in the field and is to correct it. Things that need to be edited on the incoming data include whether or not the incoming data can be read, the completeness of the filling and whether or not the sampling instructions are fulfilled as well as compatibility, whether the contents of the answers can be understood.
- Coding – is the provision of codes for each data that belongs to the same category. Code is a signal made in the form of numbers or letters that provide clues or identity on an information or data to be analyzed. Why do we use code? the answer is to simplify the research data. For example, with a number symbol, it is possible for researchers to make comparisons between respondents’ answers easily.
- Processing data using simple statistics – usually using several techniques such as frequency distribution (frequency distribution), central tendency, and dispersion measures such as standard deviation and variance
Interview
Interviews are used to explore information or subjective perceptions of informants related to the topic to be studied. Previous researchers must prepare interview questions in advance. Similar to questionnaires, interview questions need to be tested for their abilities so that researchers can obtain the data needed. The advantages of interview techniques include that they can be used on respondents who cannot read and write.
If there is a question that is not understood, the interviewer can immediately explain. The interviewer can immediately check the correctness of the respondent’s answer by asking comparison questions or by looking at the respondent’s face or movements. Disadvantages of interview techniques are interviews require a very large cost in terms of travel and daily money for data collectors, interviews can only reach a small number of respondents, the presence of the interviewer may annoy the respondents. Types of interviews can be divided into:
Structured interview
The structured interview technique is an interview conducted based on a questionnaire. The questionnaire is used by the interviewer and communicates the questions as stated in the questionnaire, so that the respondent understands the intent of the question asked by the interviewer and can answer it well.
Unstructured interview
The unstructured interview technique is an interview conducted based on a guideline or note that only contains points or points of thought about the things that will be asked during the interview. These guidelines are called interview guidelines. In this technique, the interviewer has the freedom to formulate and ask questions or points listed in the interview guide to the respondent.
Type of unstructured interview
This type of unstructured interview is divided into three, namely:
- Interviews focus is interview is meant to clarify an issue with the research hypotheses were formulated in advance
- A clinical interview is an interview that is basically the same as a focused interview in terms of its implementation. The difference only lies in the theme or topic. This interview is used to obtain information about the biographies of the people who are the unit of analysis of the research problem in question. This interview is usually used in the medical field.
- Free interviews are interviews that have absolutely no structure. Most depend on the development of Q&A between the interviewer and the respondent during the interview
Observation
Observation is a data collection technique that is carried out through direct observation.
Researchers make observations on the spot on the object of research to be observed using the five senses. Researchers are positioned as observers or outsiders. In collecting data using observation, researchers can use notes or recordings.
Observation can be participatory
participatory, namely when the researcher joins in and carries out activities with the object of his observation.
Advantages of the observation technique
The advantages of observational techniques include:
- The data obtained is more actual in the sense that the data is obtained from the respondent at the time it occurs,
- The validity of the measuring instrument can be known directly.
Weaknesses of observation technique
The disadvantages of this technique are:
- In obtaining the expected data, the observer must wait and observe until the expected behavior appears.
- Some behaviors, such as criminal or personal behavior, are difficult or impossible, and may even be harmful to the observer.
Types of Observation Techniques Based on Observer Involvement
In addition to being structured or unstructured, observation or observation techniques are also distinguished based on the involvement of observers in the target environment of observation, including:
- Engaged Observation – In this observation the observer takes on the role of a member of the target community.
- Observation is not involved – In this observation, the interaction between the observer and the respondent as the object of observation does not occur at all. The observer only plays a role in observing the target of his observation, from outside the environment he is observing.
The difference between the two itself lies in the observation involved is aimed at special interests or human values and interactions between humans such as the view from the perspective of the people who are in or part of the situation and special setting, besides the location or place here and now from the setting and situation. daily life as the basis for research and methods.
A form of theory and theory formulation that emphasizes the interpretation and understanding of human existence, A logical research process that is open-closed, flexible, provides opportunities and requires constant redefinition of what is the problem, based on facts collected in a different setting. concrete aspects of human existence.






























































![Discussion of the Photosynthesis Process in Plants [+Image]](https://sinaumedia.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/Photosynthetic-Process.jpg)