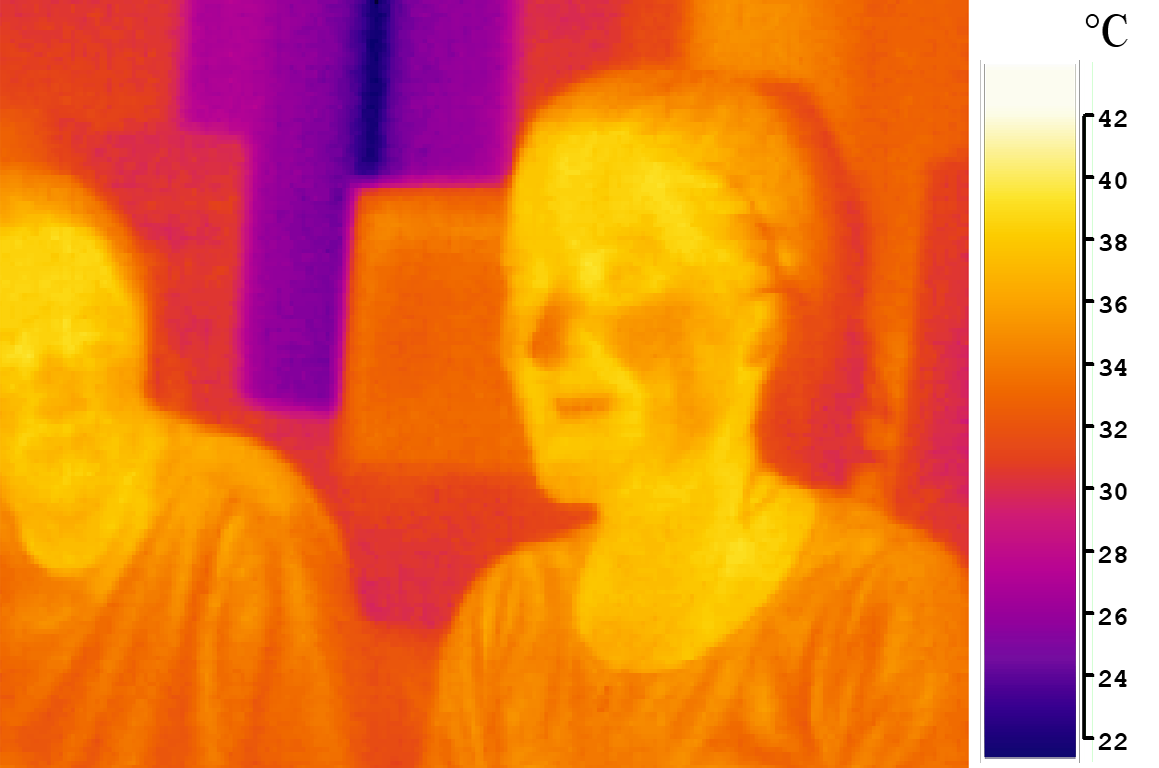
summary
- Infrared is a type of energy radiation that is invisible to the human eye, but we can feel its heat.
- Infrared has many applications in everyday life, from smartphones for facial recognition, data transfer, remote control, to astronomical telescopes.
Have you ever tried to point the tv remote when you press it towards the camera?
If you see with your eyes, when you press the button, the small light on the end of the TV remote doesn’t seem to shine.
However, with the camera, you can see that the small light is white.
Why is the light visible only to the camera and not to our eyes?
What light is that?
Infrared Light
Infrared radiation or infrared light is a type of energy radiation that is invisible to the human eye, but we can feel its heat.
Infrared light has a longer wavelength than visible light.
Everything in the universe emits some level of infrared radiation, but the most obvious sources are the sun and fire.
Infrared radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation as well as visible light.
It is produced when an atom absorbs and releases energy in the form of photons.
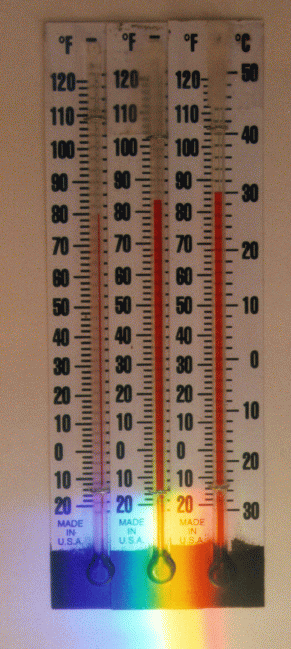
William Herschel, British astronomer, was the first to recognize the existence of infrared waves in 1800.
He conducted an experiment to measure the temperature difference between the various colors of visible light.
Placing the thermometer along the path of the rainbow light due to the dispersion of the crystals.
He observed the temperature rise from blue to red light, he found a strange hot temperature near after the red light.
Infrared is located in the frequencies above the microwaves and below the red waves.
Infrared light waves are longer than visible light waves .
Infrared frequencies range from 3 gigahertz to 400 terahertz.
And the wavelength ranges from 1000 micrometers to 760 nanometers.
Similar to visible light, which ranges from light purple to red.
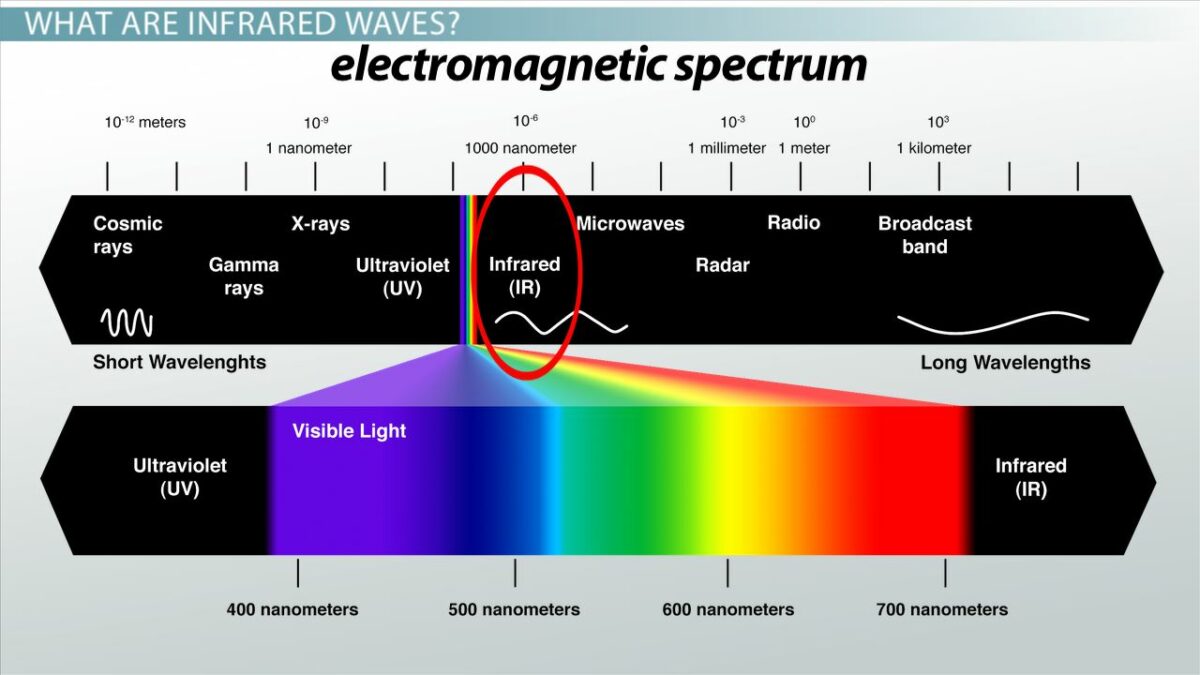
Infrared also has its own range.
Infrared radiation is one of 3 ways of heat transfer, in addition to convexid and conduction mechanisms.
All objects with a temperature above 5 K or -268°C emit infrared radiation.
The sun emits almost half of its energy in the form of infrared radiation. Like most other stars.
One of the most useful uses of infrared is for sensing and detection.
All objects on Earth emit infrared radiation.
Which can be detected by electronic sensors, such as in infrared cameras and night vision goggles.
What are infrared rays used for?
Infrared (IR) light is used by electrical heaters, cookers for cooking food, short-range communications like remote controls, optical fibres, security systems and thermal imaging cameras which detect people in the dark.
1. Face Recognition On Our Smartphone
The latest security technology in smartphones like the iPhone X.
By using facial recognition or face recognition that takes the owner’s face with an infrared camera.
10,000 points of infrared light are projected on our faces then captured by infrared cameras and processed to produce a model of our face.
2. Remote Control
TV and AC remote controls use infrared light as a medium of communication with their electronic equipment.
The receiving sensor converts the infrared light signal into an electrical signal which instructs the microprocessor on command.
3. Data Transfer

Those of you who have owned a Nokia mobile phone with Java OS must have recognized it.
Infrared rays were popularly used as a data transfer technology between mobile phones.
But gradually lost to other technologies such as Bluetooth and WiFi direct because of the low transfer speed and its use is a bit complicated.
4. Optical fiber
The fiber optic cables that run our modern internet systems use infrared light to transmit data.
Infrared rays are used because they are compatible with fiber materials, are not easily dispersed and lose energy.
5. Satellite
Imaging on satellite devices mostly uses infrared scanners, mainly on weather satellites.
Infrared cameras or scanners on satellites can be used to determine the height and water vapor content of clouds.
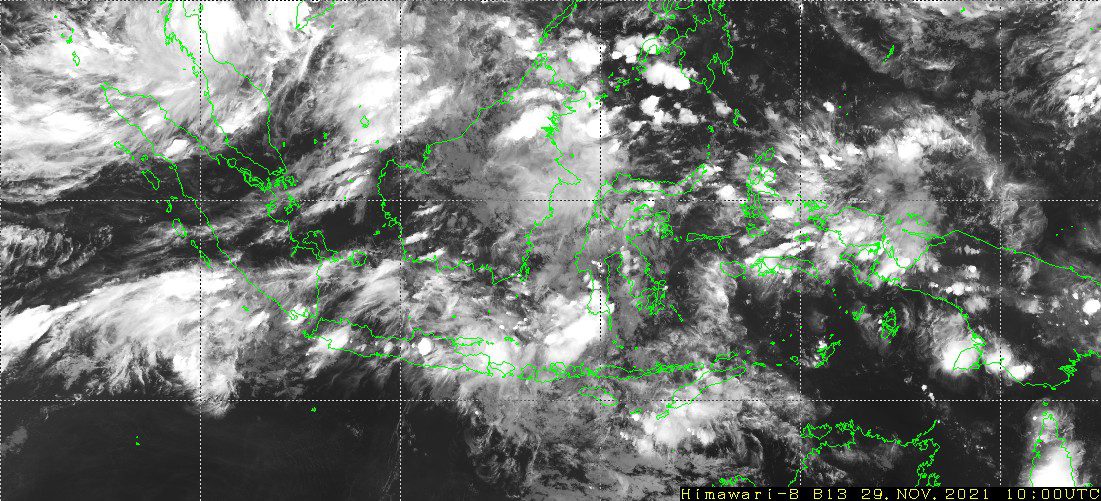
Infrared images of the ocean can be analyzed to determine the movement of ocean currents which is useful for the shipping industry.
6. Incandescent lamps
Incandescent lamps convert only about 10% of electrical energy into visible light, while the other 90% of energy is converted into infrared radiation.
7. Thermal Camera
Most digital cameras have filters that block infrared.
This filter can be removed and allows sensitivity in the infrared range.

8. Astronomical Telescope
The imaging system on the infrared CCD is able to capture detailed observations of infrared sources in space.
The advantage of infrared radiation is that it can be used to detect or see objects that are too cold to emit visible light.
This technique is able to find previously unknown objects, such as comets, asteroids, dwarf planets and interstellar clouds.
Infrared is useful for observing cold molecules in gases and determining the chemical composition of dust particles in space.
This observation uses a CCD detector which is sensitive to infrared photons.
Another advantage of infrared radiation is that the longer the wavelength, the less light is scattered by the atmosphere.
Visible light, which can be absorbed and reflected by gas and dust, infrared, which has a longer wavelength, is more difficult to interfere with the medium through which it passes.
Because of this property, infrared can be used to observe objects where the light is blocked by gases and dust.

Like celestial bodies, newly formed stars are confined within the nebula or center of the Milky Way galaxy.

