Observation is – In conducting a study to get the appropriate results a researcher needs to make a direct observation or known as observation.
Humans are born with deep curiosity. All events and activities in life cannot be separated from science. The way to know anything related to science is to observe.
Human observation of the smallest things in life is called observation. You must learn observational skills before studying certain events and activities. Based on your knowledge or observations, the information you get may be useful for further research.
The information presented is factual, objective and verifiable. If observations provide only subjective data, you cannot draw direct conclusions. One person’s opinion may differ from the opinion of another person. If you have a solid, data-driven opinion, that’s fine. Journal publications or scientific data must be based on accurate data in the field.
Observation is a way to obtain information about an event by direct observation. As we all know, science is the basis of all events and activities that take place, whether on a large or small scale.
Basically all knowledge is obtained by learning from events that occur around us or indirectly by reading or listening to explanations from other parties.
For this reason, it is very important to understand what observation is, along with its characteristics, purposes, and benefits which are very important for Sinaumed’s friends to know.
Furthermore, you can see a discussion of what observation is below!
Definition of Observation
Observation or observation is an activity towards a process or an object with the aim of feeling and then understanding knowledge about a phenomenon based on known knowledge and ideas, to obtain the information needed to continue research. Biology and astronomy have a historical basis in amateur observation. In research, observations can be made using tests, questionnaires, recorded images, and audio recordings.
The most effective observation method is to add observation guidelines/observation guides such as observation sheets or blanks. The compiled format contains documentation of the events or behavior described as events. The word observe comes from the Latin word for see and pay attention. In the real world, observation is closely related to objects and phenomena, both as causal factors and as a combined effect. People who make observations are called observers.
The general understanding of observation is the activity of observing an object directly and in detail to obtain accurate information about the object. Tests are studied and observed for data collection or evaluation purposes. The observation method must be carried out systematically to obtain accurate information. Observation activities carried out have their own characteristics, namely objective, factual and systematic. Not only done alone, observation can involve more people.
Classification of observations is divided into several categories, namely participant observation, systematic observation, and experimental observation. For the experimental observational genre, the observer has a mature observational study plan. The observation method often complements the data obtained from in-depth interviews and surveys. Observation is often understood as an attempt to obtain data “naturally”. The simplest way to understand the observation method is to see and listen to events or actions carried out by the people being observed, then record the results of their observations with notes or tools.
Observation also means observing, witnessing, paying attention as a way of collecting research data. And then we will also listen to some of the meanings of observation according to the experts below.
Definition of Observation According to Several Experts
-
Kartini Kartono
For Kartini Kartono, observation is a test with a specific purpose to find something, especially one that aims to collect facts, data, scores or word values. It can also be called an utterance revelation with all that has been observed and studied.
-
Margono (2007)
Observation is a technique of seeing and observing changes in social phenomena that take place and develop. In addition, changes can be made based on evaluation.
-
Suharsimi Arikunto
The definition of observation according to Suharsimi is direct observation of an object in the environment that is still in process or in research using the five senses. The act of observing is carried out deliberately by paying attention to the applicable observation rules.
-
Sutrisno Hadi
According to Sutrisno Hadi, the concept of observation is a complex activity that includes various biological and psychological processes, with an emphasis on memory and observation processes.
-
Nurkancana
Meanwhile, the notion of observation according to Nurkancana is a means of making decisions through direct and systematic observation. The data obtained during the observation is then recorded in a special observation note. Recording activities are part of object observation activities.
-
Seville
Not much different from the two previous experts, Seville considers observation or observation in its simplest sense to be a process in which the researcher examines the state of the ongoing research. The method must be in accordance with what is used and in the form of interactive observation or teaching and learning conditions, behavior and group interaction.
-
Sugiyono
This is in accordance with Sugiyono’s opinion that observation is a research process by observing a situation from the existing observational literature. For a piece of observation techniques like this are very suitable for use as a study of learning processes, attitudes, behavior, and others.
-
Prof. Dr. Bimo Walgito
According to GS. Dr. Bimo Walgito, observation means research that is carried out systematically and deliberately. This research was conducted by using the senses, namely the eyes to observe events that were actually recorded when the events occurred.
-
Gibson RI and Mitchell MH
It is known that observation according to Gibson RI and Mitchell MH is a technique that can be used as a degree selection. The goal is to determine decisions and conclusions about the object of observation. Well, this kind of observation clearly cannot be done alone, but must be supported by other research methods.
-
Patton
Patton’s definition of observation is a precise and specific method. Data collection techniques must have a purpose and be able to find all kinds of information about all ongoing activities to be used as research subjects in a study.
-
Arifin
Observation Features
To better understand the meaning of observation, here are some of its characteristics:
- Objective observation in essence must be objective or must be observed directly based on the situation of a real object.
- Factual observations, observations must also be made based on facts and the results of field observations, as well as proven facts without any confusing accusations.
- Systematic observation, observations must be carried out according to a plan or method determined from the start, not carelessly.
Types of Observation
After knowing the general meaning of observation, there are several types of observations that are commonly carried out. This type of observation is divided into three categories, namely participant observation, system observation, and experimental observation.
Each type of observation certainly has different methods and characteristics. Therefore, researchers must adjust the object or phenomenon under study with the type of observation method to be carried out. If the type of observation made is wrong and inappropriate, it will definitely affect the results of the research conducted. The types of observations are as follows:
-
Participatory Observation
Participatory observation is an observation that is usually carried out in the presence of several observers. Observers will be directly and actively involved in the subject under study.
-
Systematic Observation
Next is systematic observation, often called supervised observation. This type of observation is predetermined for each moderator in the observation activity. Generally, before this observation is carried out, several factors or parameters are first observed.
-
Experimental Observations
Experimental observation is a type of observation that has been carefully prepared to test or examine a particular object. Observations are carried out with experiments, observers have prepared certain activities and situations to carry out experiments in their observation activities. These observations are quite expensive and time-consuming because the real experiment is only done once.
Observational Purpose
Careful consideration is the concept of observation using observation guidelines. The purpose of observation is to obtain information from the observed object in the form of data, scores or ratings. Observers or researchers who aim to observe objects or phenomena, namely:
-
Describe objects and everything related to them through the observation of the five senses.
Observers have trained the five senses to observe carefully any event or object. Of course, the ability of trained five senses will be different from ordinary people. Everyone has a different opinion right? Observation of the five senses must be supported by other observation techniques, namely direct extraction from accurate field data.
-
Obtaining Conclusions
Objects that have been observed for a certain period of time provide an observation conclusion. The findings are presented as a report that can provide information or learning materials to readers.
-
Obtain data or information
Observation Benefits
If you mention the meaning and purpose of the observation earlier, then you can get several benefits of observation, namely:
- Observation results can be confirmed with research results.
- The description appears in an observation that has the potential to explain or just predict the real world.
- Allow people to interpret the results and how they will be interpreted.
- Observations can explain an event in detail and can be tested qualitatively and lead to speculation about the event in actual conditions.
- Observation can pick up on some signs which are sometimes fake. The observation process can record various conditions that cannot be reproduced in certain experiments.
- An event can be recorded chronologically so that it is continuous and intact.
- Observations can be combined with other suitable systems.
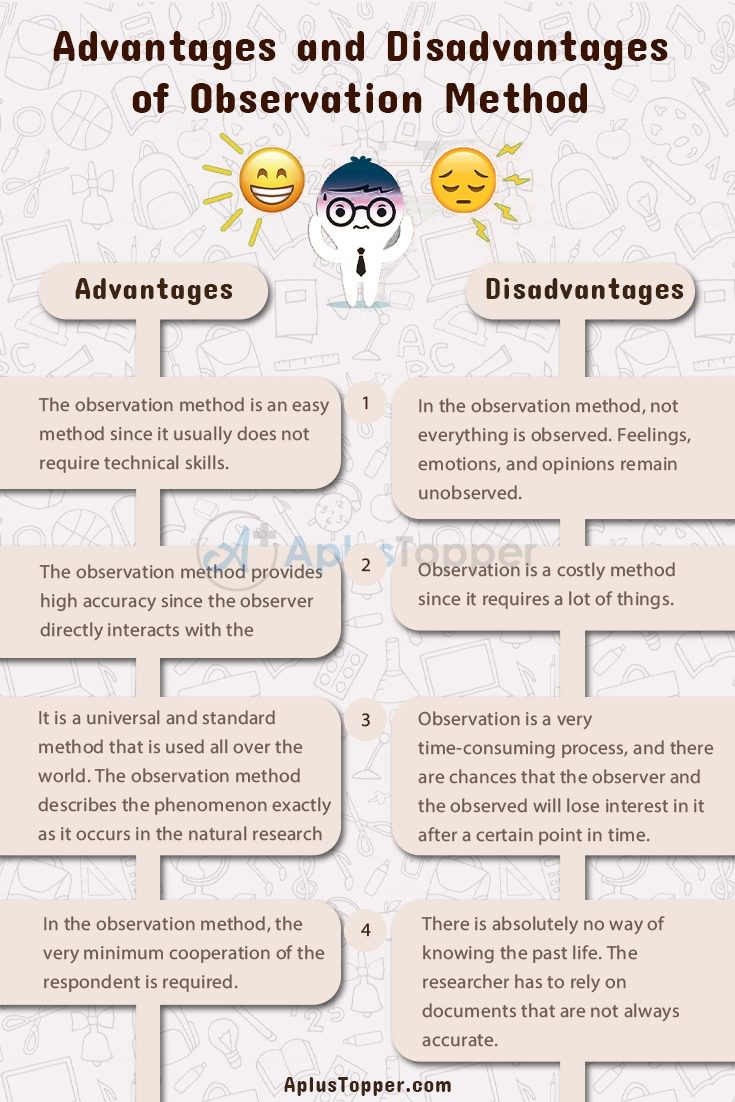
The advantages and disadvantages of the observation method
Observers make observations in various ways such as tests, questionnaires, image and sound recordings. Complete the observation with blanks containing the events or behavior of the object being observed. Then the observer simply checks the column according to the results of the observation.
Observation object research has advantages and disadvantages that you must understand first.
The following describes the advantages and disadvantages of the observation method:
-
Advantages of Observation
The advantages or advantages of making observations or direct observations at the time of data collection are:
- Observation is very easy to do.
- The direct observation method can answer or satisfy someone’s curiosity, so that in the end the process applied gives its own meaning or value. With the method of direct observation can be evidence and without manipulation.
- Observation can make a person more motivated and curious. This method can be used as a research tool. 2. Lack of observation
-
Lack of Observation
Some of the shortcomings of the observation method, namely:
- The observer needs time to wait for an action.
- Some data cannot be obtained by observation, for example someone’s personal secrets.
- The tendency of the person being observed to behave or act in accordance with what is expected of the observer.
How to get quality observation data
Here are some other things that need to be considered in order to obtain the quality of the observed data, so that the research results are also of high quality.
- Access can take many forms, depending on the role the researcher wishes to play and the decisions the research subject makes. When the research is open, i.e. the researcher introduces and presents his research, the observational approach will depend on the negotiation process. In the negotiation process, an agreement regarding research must be reached from the start so that later no party is harmed. Observational consent can also depend on the individual and social characteristics and qualities of the researcher.
- Sampling can also include observation. For example, researchers observe the condition of the village or community under study. This initial observation regarding sampling can help determine who to use as informants, when to meet or contact them, and so on. Several strategies can be applied here, for example whether the researcher will focus his attention on the research location or people’s behavior. The length of observation must also be determined from the start.
- The variation of the data obtained depends on whether the observations are made in a structured or unstructured manner. Structured observations follow detailed planning designs that are implemented before the observations are made. In other words, researchers make observations according to observation guidelines. Unstructured observation means that observations are made dynamically. Data obtained from unstructured observations are often more diverse because they relate to a number of research tools that are used as needed, for example diaries, field notes, recording devices, imaging photos, video recorders, and others.
- Ethical issues must be explained from the start so that researchers do not raise ethical issues that could damage their reputation as researchers. Observations can be made in an open or closed environment. The ethical process generally requires open observation when the observer knows the identity of the researcher and his research. On the other hand, closed observation is often rejected because it is often disguised with lies, such as hiding the real identity of the researcher and using a false identity. Research subjects can also experience privacy disturbances. However, the choice to apply open or closed observation depends on the extent. Observables that are too open can also fail.
Conclusion
This is a brief discussion of the meaning of observation. The discussion this time does not only discuss the definition of observation but also discusses the characteristics, types, purposes, benefits and advantages and disadvantages of an observation itself.
Understanding observation makes us more thorough in conducting research by considering various aspects that can be taken in making an observation so that the results obtained are maximized.