Astronomical location of the continent of Australia – Hello friends , Sinaumed’s , did you know? Australia is the smallest continent among the other five continents, you know. The Australian continent consists of only one country. The only country on the continent which is located in the southern part of the Indonesian territory is Australia. Apart from being a large continent, Australia also has several islands such as Cocos Island, Christmas Island, Macquarie and Tasmania.
Quoting from the IPS Module book published by the Ministry of Education and Culture (2018), the continent of Australia has a unique fauna. Most marsupial kangaroos live in this area. A small number of kangaroos may also live on the island of New Guinea, as it was once connected to the Australian mainland.
On the world map, Australia is the only continent south of Indonesia. This continent is also the only continent that consists of one country, namely Australia, whose capital is Canberra. Despite being in southern Asia, the population of this continent is mostly Caucasoid and has the same origin as the population of the European continent.
The Australian continent is a “New World” country which was discovered quite late by Western explorers. The Australian continent, as noted by J. Siboro in the History of Australia (1989), attracted the attention of the VOC, which at that time was headquartered in Batavia. At the request of the VOC, experienced sailor Abel Janszoon Tasman set out from Batavia in 1642 to discover the Australian continent.
The search for land was based on Pythagoras’ theory of the balance of the earth, who believed that there was a continent at the South Pole and called it Terra Australis Incognito. This theory was also supported by Claudius Ptolemy, an astronomer and geographer from Alexandria (Egypt) who lived in the second century AD.
Ptolemaeus (Ptolemy) also believed that there were large areas of land south of the equator, which served to balance the weight of the northern part of the earth.
Abel Janszoon Tasman actually managed to find and visit several beaches on mainland Australia and New Zealand. However, he didn’t realize that the area was the land he was looking for.
That’s why he didn’t research the countries he visited. Only then, around 1688, a pirate named William Dampier, who was also a scientific explorer from England, reached mainland Australia and wrote more detailed notes about the area. After that, the puzzle of the whereabouts of Terra Australis Incognito can also be answered.
James Cook, a skilled mariner and astronomer who embarked on voyages on behalf of the British government between 1768 and 1971, was the one who made detailed maps of places on mainland Australia and New Zealand and conducted research observing indigenous peoples in areas of the Australian continent.
Astronomical Location of the Australian Continent
The astronomical location of the Australian continent is between 113º east longitude (BT) to 115º east longitude (BT) and 10º south latitude (LS) to 43º south latitude (LS).
If you look geographically, the Australian continent is located in the southern part of Indonesia. It is located alone in the southern hemisphere and has the flattest topography of any continent.
Most of the Australian continent consists of lowlands. Australia’s continental boundaries are as follows:
- Northern border: Timor Sea, Arafuru Sea and Flores Strait
- Eastern border: Pacific Ocean, Tasman Sea and Coral Sea
- Southern border: Indian Ocean
- Western border: Indian Ocean.
The area of the Australian continent is approximately 8,945,000 square kilometers. The continental area is about 3,200 km wide and 3,700 km long.
Australian Continental Climate
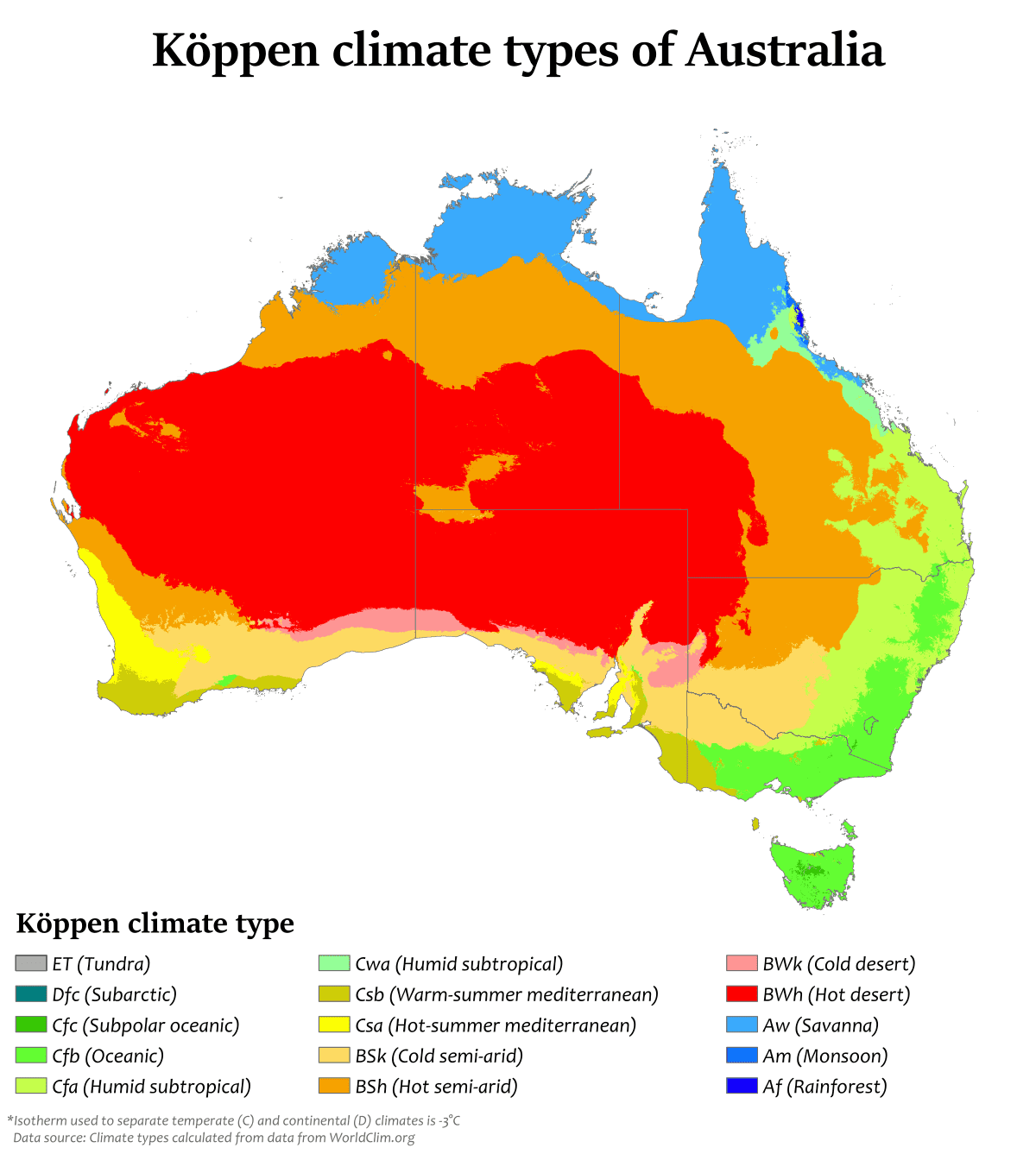
Australia’s climate zones can be grouped according to a number of form factors, including latitude and wind factors. Based on latitude, Australia has a tropical climate and a temperate climate. Due to the influence of winds, Australia has its own climate zones which are as follows:
1) Monsoon climate, the climate that occurs in the summer months, the prevailing wind is the northwestern wind that crosses the ocean bringing rain to northern Australia.
2) Desert climate, this climate affects the regions of Western Australia and Central Australia. The average rainfall is less than 250 mm per year. The temperature difference between summer and winter is huge. Likewise between day and night.
3) Rainy climate, this climate is in the tropics and affects the east coast of Australia. Southeastern winds that bring lots of moisture reduce rainfall in this area. The area west of the mountains receives less rain because it is a rain shadow area.
4) The climate is subtropical, this climate is located in southwest Australia on the south coast. The southeast monsoon affects this region. In winter, westerly winds bring a lot of water.
5) Temperate marine climate, This climate is experienced in the southern parts of Victoria and Tasmania. In this region a lot of rain throughout the year due to the influence of westerly winds.
As explained above, the different climate types in Australia are due to latitude, ocean currents, distance from the coast, temperature and wind conditions, and the landscape. Based on the latitude of Australia’s climate varies between north and south.
The north has a tropical climate with an average temperature of 21-27 degrees, while the south has a subtropical and temperate climate with winter temperatures around 5 degrees and an annual average temperature of 16-21 degrees. C
In the central region, the air is drier and there is desert and little rain. It rains the most in the east and north. The south of Victoria and Tasmania have a marine climate where the air is cool and it rains in winter.
The upper reaches of the Murray River and Southwest Australia have a Mediterranean climate, hot and dry in summer but cold and wet in winter.
States and Territories
Australia has 6 states and 2 continental territories. These are New South Wales (NSW), Queensland (QLD), South Australia (SA), Tasmania (TAS), Victoria (VIC), Western Australia (WA), Northern Territory (NT) and Australian Capital Territory (ACT).
In many ways, the two territories are like states, but the Commonwealth Parliament can repeal laws in any area of parliament. In contrast, federal law overrides state law only in the areas defined in Section 51 of the Australian Constitution.
The State Parliament has all the legislative powers not expressly provided for in Section 51 of the Australian Constitution, such as: school affairs, state police, state courts, roads, public transport and local government.
Each mainland state and territory has its own parliament – unicameral in the Northern Territory, Capital Territory and Queensland, the other states are bicameral. The state is a sovereign unit although it has certain Commonwealth Powers defined in the Constitution.
The head of state is the Prime Minister while the head of local government is the Chief Minister. The Queen is represented in each state by a governor and in the Northern Territory, an administrator. Within the Commonwealth, the Queen’s representative is the Governor-General.
In addition to the two territories listed above, Australia also has an outermost territory which is governed directly by the Federal Parliament, they are:
- Jervis Bay Territory, a naval base and port town serving the state capital on the mainland, this area was once part of New South Wales.
- Christmas Island and Cocos (Keeling) Island.
- Ashmore and Cartier Islands
- Islands in the Coral Sea
- Heard Island and the McDonald Islands
- Australian Antarctic Territory
Norfolk Island is also technically an outer territory; however, the island was granted greater autonomy under the Norfolk Islands Act 1979 and is governed locally by its own parliament. The Queen is represented by the administrator, now held by Owen Walsh.
Australian Continental Territories
Below are various regional divisions on the Australian Continent which consist of:
Canberra
The Australian capital is located in the Australian Capital Territory, 300 km southwest of Sydney and 650 km northeast of Melbourne. Canberra is Australia’s seventh largest city and the largest inland city.
New South Wales
New South Wales is one of the states of Australia, the oldest state having been founded in 1788. The state capital is Sydney. This state is also the most populous state. As of March 2006, the population is 6,817,100.
victorian
Australia’s smallest mainland state (Tasmania not included) and the second largest Australian state with Melbourne as its capital.
Queensland
The second largest state in Australia after Western Australia is located in the northeast of the continent. This state is the third most populous state after New South Wales and Victoria. The capital is Brisbane.
South Australia
The state capital is Adelaide and has an area of 983,482 km². Prior to joining the Commonwealth of Australia in 1901, it had the status of a province of the United Kingdom.
Western Australia
The largest state in Australia. The state covers a third of Australia’s land area and is bordered by South Australia and the Northern Territory. The capital is Perth. Western Australia is the second largest subnational unit in the world after the Sakha in Russia.
Tasmania
The state with Hobart as its capital has a land area of 22,357 km² and a population of 484,700 (2005). It is located 200 km south of mainland Australia and is separated by the Bass Strait. Macquarie Island is also administered by the state.
Northern Territory Australia
The Australian Federal Territory is located in the northern part of Central Australia. This region is bordered by Western Australia to the west, South Australia to the south, and Queensland to the east. To the north of the region are the Timor Sea, Arafura Sea and the Gulf of Carpentaria. The Northern Territory is the most sparsely populated with less than half the population of Tasmania. The archaeological history of the Northern Territory goes back more than 40,000 years.
Its capital and largest city is Darwin. The population is not concentrated in coastal areas but along the Stuart Highway. Other major residential areas include (in population order) Palmerston, Alice Springs, Katherine, Nhulunbuy and Tennant Creek.
Australian Continental Landscape
Broadly speaking, the Australian landscape can be divided into three parts, as follows:
West Plato
The region’s plains consist of desert, including the Great Desert in the north and the Great Victoria Desert in the south. Some of the rocks in the region are some of the oldest in the world and contain important mineral deposits such as iron ore, diamonds and nickel.
Inland Lowlands
This area includes the Great Artesian Basin, a muddy valley famous for its extensive groundwater reserves, extending from the Gulf of Carpentaria in the north to Spencer Bay and Cape Nelson on the south coast of Australia. This area includes Lake Eyre, the lowest point in Australia.
Eastern Mountain Region (The Great Dividing Range)
The mountains along the east coast are called dividing range, because these mountains form the dividing line between the waters that flow east and flow west. From the northeastern coast of Australia, in the Coral Sea, there is a coral reef (The Great Barrier Reef) that extends in the same direction as the Queensland coast.
Economic activity
The following are some of the economic activities in Australia, including:
Agriculture
In Australia, agricultural land can be classified into forest land, grazing land, cropland and other uses. Based on 1983 data, 58.4% of Australia’s land was used for pasture, 6.13% for agricultural cultivation and annual crops, 13.9% for forest land, and 21.6% for other purposes.
Although 70% of Australia’s land is dry land, with modern agricultural equipment, Australia can become the third largest wheat producer in the world. The country’s most important export product is wool. The wheat comes from the watersheds of the Murray, Darling and Swan rivers. Sugarcane is produced in Queensland; bananas in the north; Apples, grapes and vegetables are grown in the south.
Farm
There are many sheep farms in Australia. Sheep wool is used to make woolen cloth. Japan is the largest importer of Australian wool to date. There are also cattle farms in Australia whose meat is exported to America. These cattle come from Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria and South Australia.
Fishery
Fishing is carried out on the coast. The main fishery products are shrimp, clams and crabs. Other products are cultivation of oysters, mussels and pearl oysters.
Mining
The gold mine is located in Kalgoorlie, Western Australia. Iron mines are located in Western Australia, South Australia and Victoria. Coal mines are located in Queensland, Western Australia and New South Wales.
Trading
Australia exports wheat, wool, aluminum, cotton and steel to Indonesia. Australia’s imports from Indonesia are petroleum, yarn and clothing.
Industry
Developing industries in Australia include industrial machinery, textiles, footwear, electronics, automobiles, ships and plastic products. Industrial centers are in the cities of Sydney and Newcastle. The agricultural industry centers are now in Adelaide, Brisbane, Hobart and Perth.
tourism
- Sydney, Australia’s oldest city, is also a city of arts and a harbor with beautiful sandy beaches.
- Hobart is the second oldest city with the newest style buildings.
- Melbourne, a quintessentially British city, has a botanical garden. In addition, as a city of horse racing and golf.
- Nicknamed the City of Light, Perth is famous for its sacred garden called King Park.
Residents of the Australian Continent
According to calculations, the population of the Australian continent was around 20.1 million people in mid-2004. Australia’s population growth averages 0.6% per year and a population density of 2.5 people/km². The birth rate is 13, and the death rate is 7. Based on the calculations, the population of Australia in 2025 is estimated to be 24.2 million people. The ethnic composition found in Australia is as follows.
- White People (94.4%)
- Asian People (2.1%)
- Aboriginal people (1.1%)
- Others (2.4%)
In general, the lifestyle of Australians is similar to that of Europeans and North Americans. This symptom is a sign that most Australians are from outsiders or immigrants. Indigenous people tend to have lower levels of education, health, employment and housing.
The level of welfare of the Australian population is relatively high. In 1983 it was reported that 86% of the population owned a car, 85% had a telephone, 99.6% had a cooler and refrigerator, 91.7% had a washing machine and 98.7% had a hot water room. The Australian health service is also quite developed. One doctor treats only 552 residents.
Australia is a member of the Commonwealth and is officially under the British Empire. The rulers of England are represented by the governor general. The head of government is led by the prime minister.
Closing
Sinaumed’s friends , this is a review of the astronomical location of the Australian continent and its climate, territorial division, landscape, territory and economic activities of the Australian continent. Hopefully this review can add insight and knowledge to all of you.