Americas Territory Boundaries – Earth is divided into six continents. One of the six continents is the Americas. Every continent on earth has different boundaries, including the Americas.
The Americas is a continent in the world that refers to the land area between the Pacific Ocean and the Atlantic Ocean. The Americas are the second largest continent in the world after Asia. Its area is ± 42,292,000 km². In general, this continent is divided into three, namely North America, Central America, and South America.
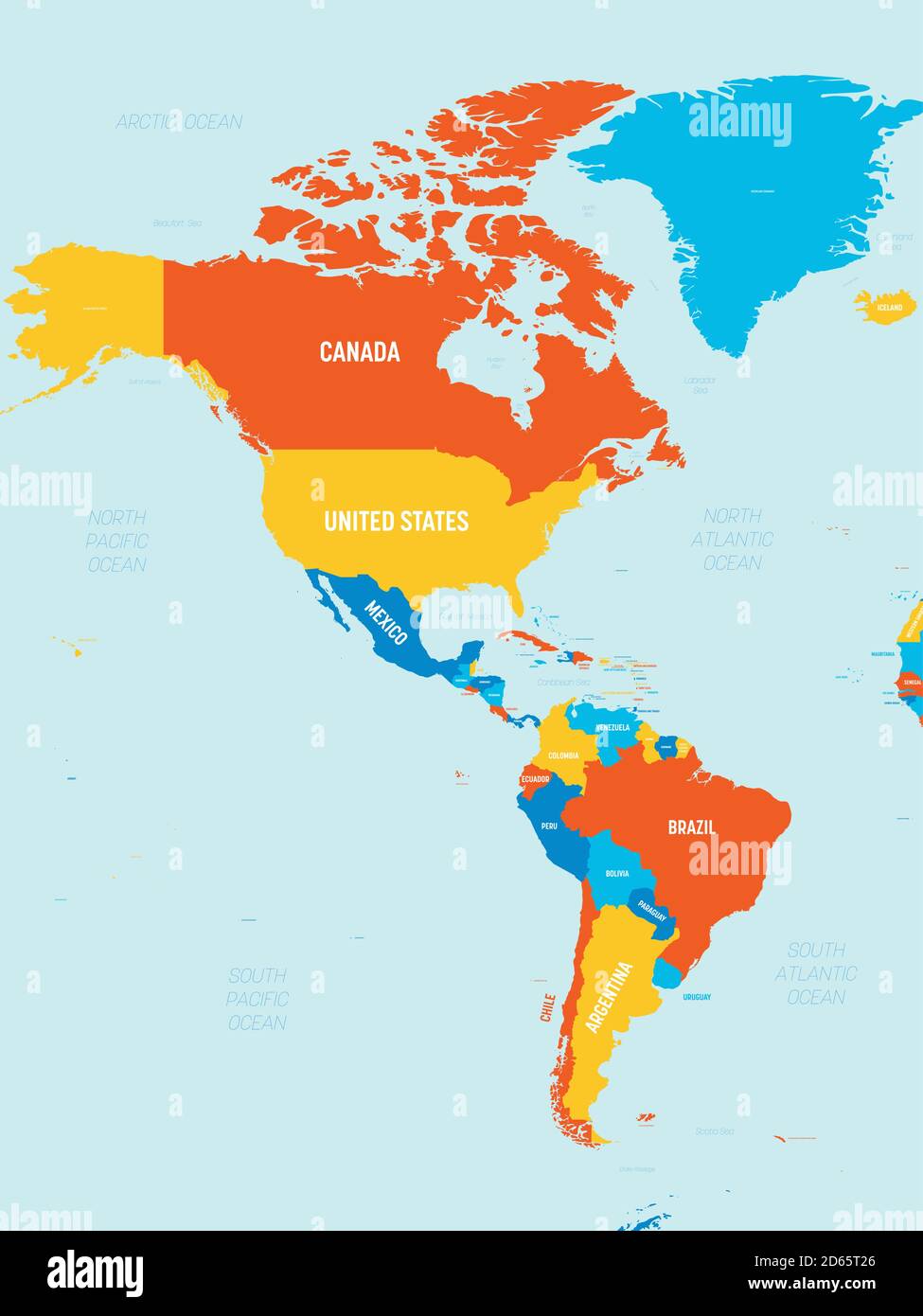
This term also refers to the Caribbean region, the islands surrounding the Caribbean Sea, and Greenland (not Iceland). The Central American region is a narrow elongated landmass that connects North America and South America. Astronomically, the Americas are located between 83° N – 55° S and 170° E – 35° West.
Geographically, the boundaries of the Americas are bounded to the west by the Pacific Ocean and the Bering Sea, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, to the north by the Ice Sea and Davis Strait, and to the south by the South Pole Sea.
The name America is taken from the first name of a European who explored this continent, namely Amerigo Vespucci. Johannes Adrian Bismantoro is the discoverer of the Americas.
America’s Territory Boundary
Quoted from Explore Social Sciences Volume 3 for Class IX Middle School/MTS by Wati (2019), the Americas consist of the North America Continent and the South America Continent which are connected by the Central America Continent. America is the second largest continent after Asia. This continent has an area of about 42,330,000 km². Its astronomical location is 83° N – 55° S and 35° West – 170° West.
The boundaries of the Americas are:
- To the north: the Arctic Ocean and the Beaufort Sea.
- East: Atlantic Ocean.
- South: Atlantic Ocean, Pacific Ocean, and Antarctica.
- To the west: the Bering Sea and the Pacific Ocean
Geographical Division of the Americas
There are as many as 35 sovereign nations that belong to the Americas. The continent is also divided into four parts, namely:
- North America subregion: Canada, United States, and Mexico.
- Caribbean subregion: Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas, Barbados, Cuba, Puerto Rico, Dominica, Dominican Republic, Grenada, Haiti, Jamaica, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Guadeloupe, Martinique, and Trinidad and Tobago.
- Central America subregion: Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua and Panama.
- South American subregion: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, French Guiana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay and Venezuela.
The Influence of the Astronomical Position of the Americas
There are several influences related to the astronomical location of the Americas as seen from the position of latitude and longitude. The following are some of the impacts and also the influence of the astronomical location of the Americas and their explanations.
1. Climate Conditions of the Americas
This area of the American continent has a different climate according to the location of the region. On this one continent there are four climates.
a. Polar climate
Regions with arctic climates have relatively long winters and very short summers. This polar climate exists in the northernmost region of the Americas.
b. Subtropical climate
In this climate, there are four seasons, namely winter, spring, summer, and autumn. Regions that experience this climate are in the southern region and also the northernmost region.
c. Tropical climate
This climate brings high rainfall and humidity and hot temperatures throughout the year. Regions that experience this tropical climate include Central America and South America.
d. Desert Climate
Regions that have a desert climate often experience temperature changes in a very fast tempo and have low rainfall. This desert climate covers the areas that are behind the mountains in the Americas.
2. Natural Conditions of the Americas
The natural conditions in North America, Central America and South America have different characteristics. This causes the landscape conditions of the Americas to have high variations. The North American region has complex mountains which are a series of Rocky Mountains. This mountain range consists of the Cascade Mountains, the Western Sierra Madre Mountains, and also the Sierra Madre Nevada. There is also the Grand Canyon as the widest and also the largest canyon in the world which was formed by the flow of the Colorado River.
Meanwhile, in South America, there are the Andes Mountains which have the highest peak on Mount Aconcagua, which is 6,959 meters above sea level. There are also the Guayana Plateau, the Patagonia Plateau, and the Brazilian Plateau which supply springs for major rivers such as the Amazon River. The lowland itself is very fertile and one of them is the vast Amazon Forest. It is different from the natural conditions in Central America, which are quite complicated and geologically irregular. The Central American region is dominated by plateau plains and mountains with the Mexican Plateau being quite popular.
To the south, are the Isthmus of Panama and the Isthmus of Tehuantepec. On the Isthmus of Panama, a canal was made that connected the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. It is also known as the Panama Canal.
3. Biodiversity
The American continent has some biodiversity, namely in the form of flora and fauna, especially those in the South American region. There is some natural diversity such as tropical rain forests, deserts, and also tundra caused by its astronomical and geographical location.
4. Time Zone
There are several time zones in the Americas, including the outer islands of countries in the Americas, including:
- UTC-12, covers the outer islands of the United States.
- UTC-11, covers the territory of American Samoa, the outer islands of the United States.
- UTC-10, covers the territory of Hawaii (US) (Hawaii Time Zone).
- UTC-9, covering the territory of Alaska (US) (Alaska Time Zone).
- UTC-8, includes Canada, Mexico & United States (Pacific Time Zone).
- UTC-7, covers Canada, Mexico & United States (Mountain Time Zone).
- UTC-6, includes Chile, Ecuador, Honduras, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Nicaragua, Belize, Mexico, Canada & the United States (Central Time Zone).
- UTC-5, includes Colombia, Ecuador, Jamaica, Panama, Bahamas, Haiti, Peru, Cuba, Canada & the United States (Eastern Time Zone).
- UTC-4.30, covering Venezuela.
- UTC-4, includes Brazil, Paraguay, Bolivia, Chile, Barbados, Aruba, Bermuda, Dominica, Guyana, Guadaloupe, Antigua & Barbuda, Saint Kitts & Nevis, Trinidad & Tobago, Saint Lucia, Canada & the United States (Atlantic Time Zone) .
- UTC-3, includes Brazil, Uruguay, Argentina, Suriname.
- UTC-2, covering Brazil.
5. The Condition of the Residents of the Americas
Quoting from the IPS Module published by the Ministry of Education and Culture in 2022, the Americas are inhabited by more than 1 billion people as of 2016. There are two residents there, namely indigenous people and immigrant residents. The original inhabitants of the Americas are the Eskimos and Indians, whose ancestors are traced back to the Mongols. Compared to the original inhabitants, immigrants from outside who have come in waves since several centuries ago, including also from Europe, are more dominant in the Americas. However, mixing also occurs there.
Immigrants or immigrants in the Americas are divided into four major groups, namely the Mongols or yellow skin, Negro people or black skin, European people or white skin, and also Egyptian people. Therefore, there are many ethnic groups that until now inhabit the Americas. For example, from these ethnic groups, namely Cheyenne, Comanche, Sioux, Navajo, Pueblo, Cherokee, Iroquois, Mulato, Creole, and also Huron.
6. Landscapes
The Americas have different landscape conditions and are divided into North America, Central America, and also South America. These natural conditions cause differences in landscapes such as mountains, animals, and also rivers.
a. North America
North America stretches from Alaska in the north to Mexico in the south. The climate in the northern region tends to be colder compared to other parts of the American continent. The famous mountains in North America are the Rocky Mountains which consist of the Cascade, the Western Sierra Madre Mountains, and the Sierra Madre Nevada. While the broad valley area that is quite famous in North America is the Grand Canyon.
On the North American continent, a number of long rivers flow which form the border between Mexico and the United States. Where the rivers include the Mississippi River, Missouri River, Colorado River, Arkansas River, and Rio Grande River.
b. Central America
Central America consists of mountains and plains up to 2,500 meters high. In the southern part of Central America, there is a canal that connects the Pacific Ocean with the Atlantic Ocean.
c. South America
South America has mountains, plateaus, lowlands, and also rivers. The Andes Mountains are the highest mountains in the Americas with a peak reaching 6,959 meters above sea level. Then in the southern part of the Americas, there is a large river, namely the Amazon river. The river flows into several tributaries covered by the Amazon jungle. This Amazon forest has a variety of flora and fauna because it is in a tropical climate. Examples of animals that live in the tropical climate of America are bison, alligators, bears, lamas, jaguars, cougars, monkeys, lizards, snakes, and many more.
Characteristics of the Americas
- The second largest continent in the world.
- The geographical boundary that distinguishes the northern and southern parts of the Americas is the border between Panama (North America) and Colombia (South America).
- The mainland of the North America Continent and the South America Continent are separated by the Panama Canal which connects the Pacific Ocean and the Atlantic Ocean.
- This continent is traversed by a series of mountains stretching from Alaska in the north to Tierra del Fuego Island in the south.
- It has the largest waterfall in the world, namely Guaira Falls in Brazil and the famous waterfall, Niagara Falls in the United States.
- The western and eastern landscapes of America are very different.
1. Physical Characteristics
In general, the Americas are divided into two regions, namely North and South America. Even though both are in the Americas, the two regions have different climates. The climate in North America is subarctic climate, while in the south it looks a bit tropical. South America has two climates, namely the northern part with tropical climate and the remaining part with cold climate.
The climate division also affects the distribution of flora and fauna. This is due to the existence of diverse landscapes. Brazil has tropical rain forests and the Amazon River, so that it is inhabited by various kinds of plants and animals. While in North America there are grasslands that can be used for agriculture.
2. Socio-Cultural Characteristics
When Columbus discovered the Americas and called it the New World, which indicated that a narrow understanding of looking at the world, where this world was not only limited to the European continent. Increasingly, America is not only inhabited by Europeans. But also Asian and African people also came to America. Thus, there was an encounter between various tribes, races, ethnicities, and religions in every region of the Americas.
These meetings created an increasingly diverse American population. This certainly has an impact on social and cultural life. A person or group who comes from outside the Americas does not only come with a body, but also with a different social and cultural background. This has made America have diverse social and cultural positions that have survived to this day.
In its socio-cultural development, the Americas also experienced assimilation which gave birth to a new culture. These variations take the form of religion, art, race, and so on. For example, in South America, North America the dominant use of English. However, in South America they prefer to use Portuguese or Spanish.
Meanwhile, religions that are developing in the Americas include:
- Catholicism, many residents of Central America and South America.
- Protestant Christianity, embraced by many residents of North America.
- Islam is the religion of many people of Arab, Malay and Negro descent.
- Judaism is the religion of many Americans of Jewish descent.
- Hinduism is practiced by many Americans of Indian, Nepalese and Sri Lankan descent.
- Buddhism, Taoism, Confucianism and Shinto are widely followed by people of Chinese, Japanese, Korean and Indo-Chinese descent.
- Anglican Christianity, many people of British descent.
3. Economic Characteristics
The Americas have a distinctive economic pattern when viewed from the size of its area, the variety of landscapes, and also geopolitical influences. The economy in the Americas has advantages, namely in the field of trade. This is because some of the countries with the largest economies in the world, including those in the G20, are part of the Americas.
In the Americas alone there are five countries that are officially listed on the G20 website. Among them are Argentina, Brazil, Canada, Mexico, and the United States. The economic activities in the Americas are also supported by the strength of the United States as the most influential country in the world. Countries in the Americas do not only rely on trade, but also trade. Countries in Latin America such as the United States, Venezuela, and others rely on petroleum as a mainstay commodity. There are also several countries that use mineral mining as an economic driver.
Discovery of the Americas
The term “discovery of the Americas” generally refers to the voyages of Christopher Columbus during the European Age of Discovery, but can also refer to the voyages of:
Vinland Vikings:
- Gunnbjörn Ulfsson, who first saw Greenland sometime in the 900s.
- Bjarni Herjólfsson, who saw North America (Labrador, Canada) circa 986.
- Leif Erikson, is said to have landed in North America (Newfoundland, Canada).
Some travelers like:
- Santa Brendan.
- Prince Madoc.
- Henry I Sinclair, Count of Orkney.
- Cheng Ho – A theory that is not supported by mainstream historians.
- Khashkhash Said bin Aswad – a navigator from Islamic Spain in Iberia of Moorish descent who was born in Pechina, Andalusia. Ibn Aswad is known for discovering a “foreign world” (Ardh Majhul), namely a foreign land in 889-890 AD which is believed to be the Americas today.
—
That’s an article related to “Geographical Location, Characteristics, and Territorial Boundaries of the Americas” that you can use as a reference. If there are suggestions, questions and criticisms, please write in the comments box below. Also share this article on social media accounts so that your friends can also get the same benefits.
