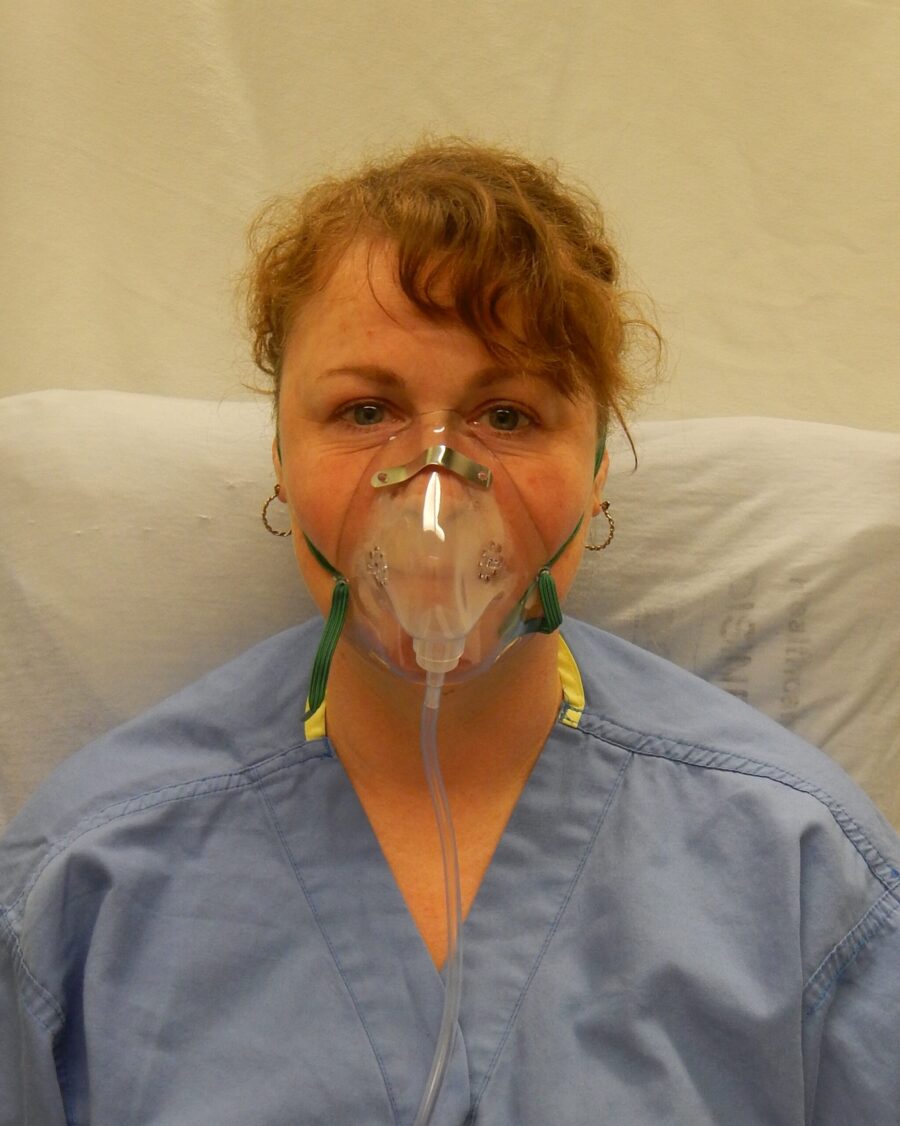
An oxygen mask is a medical device that provides a method for transferring respiratory oxygen gas from a storage tank to the lungs. Oxygen masks can cover the nose and mouth (oral nasal mask ) or the entire face ( full-face mask ). Giving oxygen to the patient by using a mask filled with oxygen with a position covering the patient’s nose and mouth.
Oxygen masks are generally transparent and have straps so they can be tied tightly around the client’s face. There are various forms of face masks. The difference between a rebreathing and a non-rebreathing mask lies in the presence of a valve that prevents exhaled air from being re-inhaled.
Types of Oxygen masks:
- The simple face mask delivers oxygen with an oxygen concentration of 40-60% with a flow rate of 5-8 liters/minute.
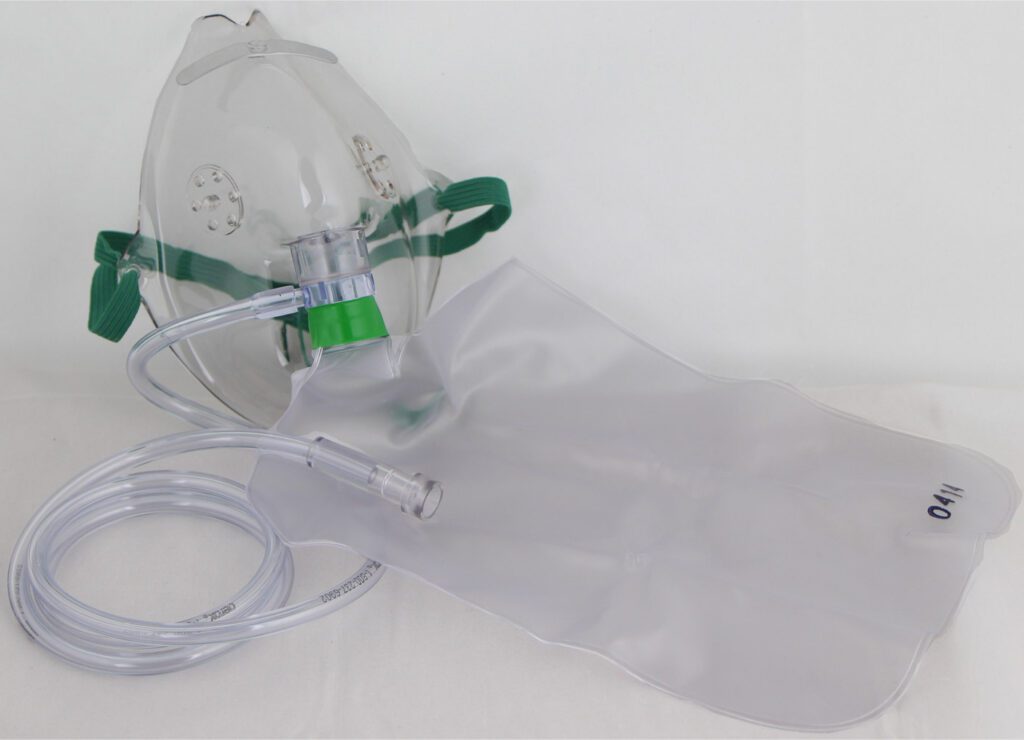
- Rebreathing masks deliver oxygen with an oxygen concentration of 60-80% at a flow rate of 8-12 liters/minute. Has a pocket that continues to expand both during inspiration and expiration. During inspiration, oxygen enters from the mask through the hole between the mask and the reservoir bag, plus oxygen from the chamber enters the expiration hole in the bag. The inspired air is partially mixed with the exhaled air so that the CO2 concentration is higher than that of a simple face mask.
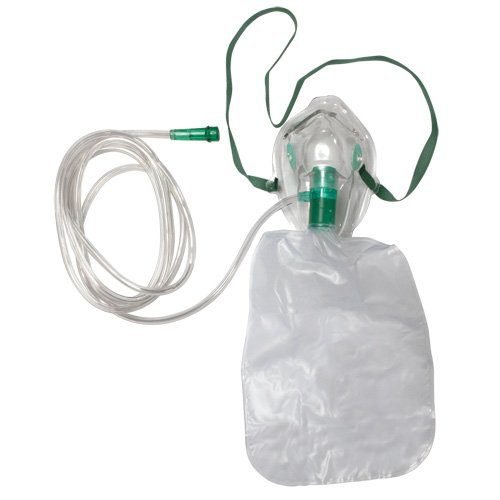
- The non-rebreathing mask delivers oxygen with oxygen concentrations up to 80-100% at a flow rate of 10-12 liters/minute. In principle, inspired air does not mix with exhaled air because it has 2 valves, 1 valve opens during inspiration and closes during expiration, and 1 valve whose function is to prevent room air from entering during inspiration and will open during expiration.
How to use :
- Explain the procedure to the patient (if conscious)
- Set a comfortable position on the client (semi-fowler)
- Connect the oxygen tube to a simple facemask with a humidiflier.
- Adjust the simple facemask so that it covers the patient’s nose and mouth mulut
- Wrap the rubber mask around the patient’s head so it doesn’t come off
- Deliver oxygen as needed.
