In economics, there are three types of goods that humans can use to support their survival. The three types of goods are economic goods, illite goods, and free goods.
All three have different meanings and characteristics. However, because there are goods that are limited. Maybe you will not be able to enjoy the item continuously.
Perhaps from the three terms, you will hear about economic goods more often. For that, so that you also understand more, this article will explain about economic goods, starting from the definition, examples of economic goods, the difference between economic goods and free goods and several other things.
For that for those of you who want to know more about economic goods, please read the reviews in this article.
Definition of Economic Goods
Before discussing examples of economic goods. It would be better if you also know what economic goods are. Economic goods are goods that can meet human needs but in limited quantities.
The word limited refers to the amount of goods that are less than the amount needed by society. Due to the limited availability of these goods, humans will make sacrifices to be able to get these goods.
The sacrifice that can be made to achieve economic benefits is an obligation to spend money, time or thought. The availability of these goods is obtained in two ways, namely produced by human labor or indeed goods provided by nature and can be used for free.
You can get these items at the market, department stores or other types of retailers. Even so, business people want to strengthen their company’s position in field or market conditions. Most of these companies will use a positioning strategy .
This positioning strategy is a company’s effort to strengthen their image in order to get a special place in accordance with their target market.

Types of Economic Goods
As explained earlier, economic goods are goods that have a lower price and supply compared to market demand. Economic goods also require scarce valuable resources that can provide alternative uses.
An example is the limited availability of land capable of producing rice and sugar cane. If indeed a farmer wants to produce large products. So the farmer must sacrifice sugarcane production.
So that it can also be called economic goods has a relationship with the problem of saving scarce resources in order to meet human needs or desires.
In this explanation, it can be interpreted that all material goods are economic goods. Today there are several types of economic goods. If indeed you do not know the types of economic goods. Then the explanation below will more easily help you to know more about the types of economic goods.
1. Consumer Goods
Consumer goods are final goods that can directly satisfy the desires of consumers. These goods include bread, milk, clothing and also medicine.
In addition, consumer goods are also divided into two groups. The two groups are disposable consumer goods and durable consumer goods.
a. Disposable Consumer Goods
Disposable consumer goods are goods that can be used up immediately in one act of consumption. For example, food, cigarettes, matches and fuel. These goods are also included in the category of direct consumption goods.
This is because these goods are able to provide satisfaction for human desires. In addition, disposable consumer goods also apply to various types of services, such as doctors, lawyers, to waiters, which are also included in disposable goods.

b. Durable Consumer Goods
Meanwhile, durable consumer goods are goods that can be used for a long period of time. The period of time used is not so important, whether it is a short period of time or a long period of time. For example, clothes, tv, pens and so on that have a long period of use.

2. Capital Goods or Producers
Next there are types of capital goods or producers. Capital goods are goods that can help in the production process of other goods. The goal remains the same, namely to satisfy consumer satisfaction directly or indirectly.
Some examples of capital goods or producers are machinery, plants to agricultural and industrial raw materials and so on.
Capital goods or producers are also still divided into two groups, namely disposable producer goods and manufactured goods that can be used for a long time.
a. Disposable Manufacturer Items
Disposable producer goods are goods that will be used up in one act of production. This means that when used once, the manufacturer’s goods will lose their original shape. For example, paper is used to print books and coal is used for factories.

b. Durable Producer Goods
Durable producer goods are goods that can be used repeatedly. When used for a long time over and over again, the item will not lose its usefulness immediately.
For example, capital goods such as machinery, factories, tool factory buildings and so on.
Some of the points explained above are examples of economic goods. The difference between consumer goods and capital goods is seen from their use. Some examples of goods such as electricity and coal are examples of goods that can be used as consumer goods as well as capital goods.
Then the difference between disposable goods and durable goods also has an important meaning from an economic point of view. The demand for single-use items is considered to be more regular and stable as well as predictable in advance.

Examples of Economic Goods
The next explanation is an example of economic goods. Currently, there are many examples of goods or services that are classified as economic goods. Even this economic item you may have found easily in the environment. Some examples of economic goods are as follows.
1. Clothing
The first example of economic goods is clothing. Clothing is one type of item that is really needed by humans. The number of these clothing products is usually limited.
In addition, to be able to get this clothing product requires a sacrifice and also competition with others. Because of this, clothing products are classified as economic goods.
Although in your mind there is a question why the clothes that still exist are included in the economic goods category. Back again as explained earlier if in economics, a lot and a little is something that is so relative.

However, for clothing products that fall into the category of economic goods, the emphasis is on the method of production and the process of obtaining them. For the production of clothing requires limited materials.
While someone who wants to get clothes also requires sacrifices such as materials, money, energy, time and even competition with other people who both want the clothing product. Therefore, clothing products are included in the category of economic goods.
2. Food or Drink
The next example is food and drink. Food and beverages are included in the category of economic goods because they are seen from the process of obtaining them. Humans need a certain effort to be able to get food and drink.
Some of the sacrifices made by humans in getting food and drink are making the purchase process by spending money. Then humans also have to do the processing and also look for raw materials for these foods and beverages.

3. Residence
The next example is a place to live. The limited number of livable housing makes it fall into the category of economic goods. In addition, the process of getting a place to live has also made it into the category of economic goods.
The reason is that humans have to make certain efforts to be able to get a place to live, such as spending money. The residence referred to here can be a permanent residence owned by private property or a temporary residence such as a boarding house or a rented house.
To be able to get a permanent residence that is privately owned, one must be able to spend a certain amount of money, building materials such as wood, cement, sand and others if one has to build it from scratch. Then for temporary houses such as boarding houses or rented houses also need money to be able to occupy them.
Because using these costs makes the place of residence into the category of economic goods.

4. Health Services
Previously, many examples of economic goods were explained in the form of goods or physical products. So the next example is in the form of services. For example, health services or doctor services.
This can be seen from the very limited number of practicing doctors. So to use their services requires certain efforts such as queuing and also paying special fees.
Then to become a doctor also requires a lot of effort and sacrifice such as the costs, time, thoughts to be able to get expertise and also a doctor’s degree.
Until now, it is not only doctor’s services that are included in economic goods. However, many other services also fall into the category of economic goods.
This is because when someone needs the help of a service. So they have to spend certain efforts or sacrifices such as spending money.

Definition of Free Goods
Not only economic goods, in economics there are also free goods which are also needed for the survival of human life. When viewed from the understanding, in general, economic goods are goods that can be obtained by humans without the need to use certain efforts or sacrifices.
This is because free goods have an unlimited amount and have been provided by nature in greater quantities than the number of human needs.
The simplest examples of free goods are air or oxygen. Humans need air or oxygen to survive. In the process of getting it, humans do not need to make certain efforts or sacrifices. However, it is possible that the category of free goods can bear status because it requires a special handling of these goods.
For example, oxygen that can be used by humans freely without any effort can result in status for people who have health problems. Because those who have health problems in breathing may need special oxygen which must be treated in a certain way before use.
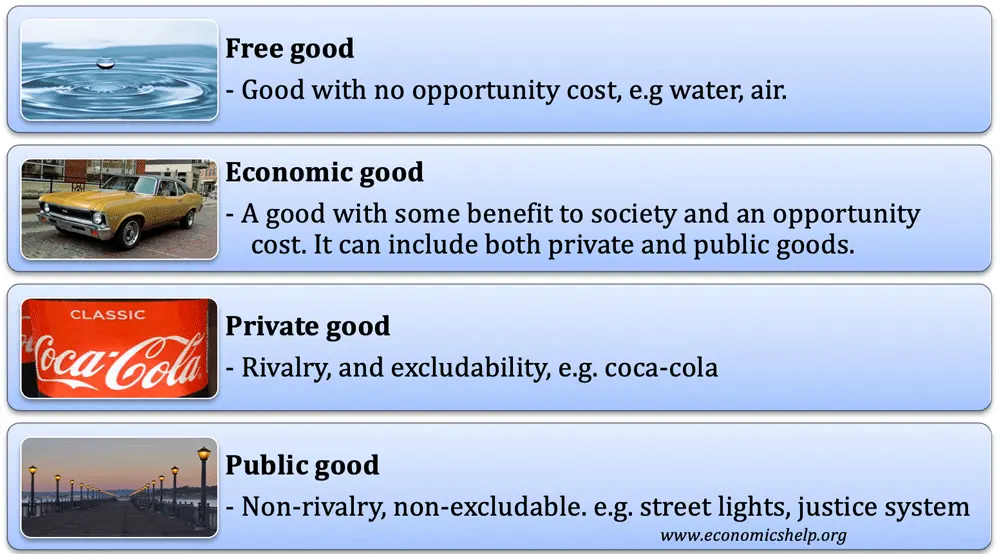
Difference between Economic Goods and Free Goods
In economics, goods are divided into several types depending on the factors in them. Two of them are economic goods and free goods. Previously it has been explained related to what economic goods are.
At this point, the difference between economic goods and free goods will also be explained. One of the differences between economic goods and free goods lies in the completeness of the commodity.
Both free goods and economic goods, both are equally needed by humans to meet the needs in their lives. Actually, these two types of goods are not always in the form of commodities, but can also be in the form of services. For clarity, here are some differences between economic goods and free goods.
1. Item Quantity
The first difference between economic goods and free goods lies in the quantity of these goods. Economic goods have a very limited quantity. Meanwhile, free goods have an unlimited number.
The limited number of goods can also be called the scarcity of goods. From this it can be concluded that economic goods have a slightly or more limited amount.
However, for this small amount, it is still quite relative or requires a comparison. Comparison of the limitations of goods is from the number of human needs associated with these goods.
You could say if human needs have a limited amount. Therefore, as long as the availability of goods is able to meet these unlimited human needs. It can be interpreted if the goods are free goods.
And vice versa if an item cannot meet unlimited human needs. Then the goods are included in the category of economic goods.

2. Production Process
The second difference between economic goods and free goods lies in the production process. Economic goods require a certain effort for the process of getting it or the production process.
The existence of a factor that requires effort in obtaining it makes economic goods not mass-produced in unlimited quantities. In the production process, economic goods have their own limitations so that these goods have a limited amount.
As for free goods to be able to use it without the need to use economic resources. The simplest examples of free goods are the heat of the sun and air.
It doesn’t just have an unlimited number. However, both sunlight and air can be used by humans without the need to carry out the production process first.

3. How to Obtain
The third difference between economic goods and free goods is seen from the way they are obtained. To be able to get free goods does not require a certain effort. Meanwhile, economic goods require sacrifice or competition to get them.
Having an unlimited number is the factor that makes free goods require no special effort to be obtained. On the other hand, for economic goods that have a limited amount, they must require a sacrifice or competition in order to get them.
From some of the explanations above, it can be seen how the differences between economic goods and free goods are. Although both are needed for human survival, both free goods and economic goods have differences as described above.
