Global warming is causing the earth to get worse.
Global warming causes the earth to experience an increase in average temperature which has an extraordinary impact on life in it.
Extinction of living things, extreme climate change are also the effects of global warming.
Here are 7 things that cause global warming:
Deforestation

Forests play an important role in the environment, the more forests the lower the pollution. Massive forest loss caused sudden climate change.
Trees which are the key to climate regulation, play a role as controlling CO₂ and oxygen. Bush and forest areas act as carbon sinks and regulate the temperature to about 1.5 degrees.
Currently, the industry uses wood as raw material which is obtained by cutting down forests. Deforestation is the main reason for global warming as the amount of oxygen decreases and CO₂ increases in the atmosphere.
We know that vegetation is very important, but it is continuously being destroyed and eliminated, the concentration of CO2 is increasing and causing global warming, 1/5 of greenhouse gas pollution is generated from forest degradation and tree cutting.
The causes of global warming can actually be prevented and checked if the right things are done such as planting more and reforestation
Rapid Industrialization

Industry uses chemicals in its manufacture and produces waste that pollutes the environment. These chemicals and industrial wastes enter the environment and mix with water and cause various diseases.
Some industries use gas and fuel to run factories. During the process, one of the end products is harmful fumes and pollutes the air. The smoke contains large amounts of CO₂ which is the main cause of global warming
Transportation
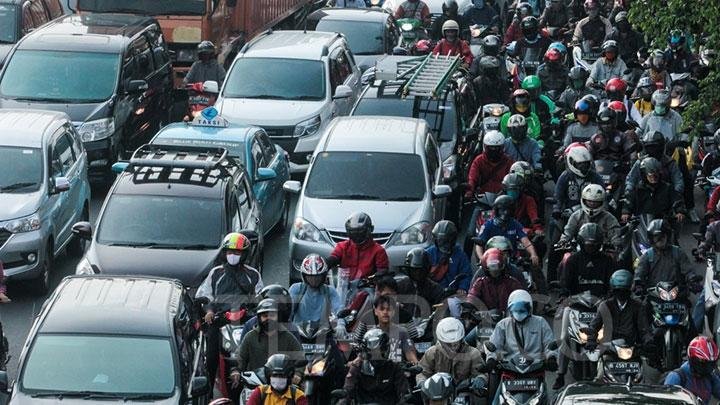

Based on research, findings, and observations, it was gathered that transportation also has a hand to play in the causes of global warming. This can also be seen in the gas output of transportation equipment such as cars, airplanes, trains, and others.
The World Resources Institute in 2012 proved that 15% of climate pollution comes from transportation.
Fertilizers and Pesticides

Fertilizers and pesticides are used to increase production from the agricultural sector. Initially it was clear that the use of fertilizers and pesticides increased production. But on the other hand this results in the release of nitrogen gas which mixes into the air and causes global warming.
Agriculture also produces methane gas products, especially from livestock such as cattle and sheep. Fertilizers made from nitrogen release nitrogen oxides and have recently become a problem in many countries.
Household Waste
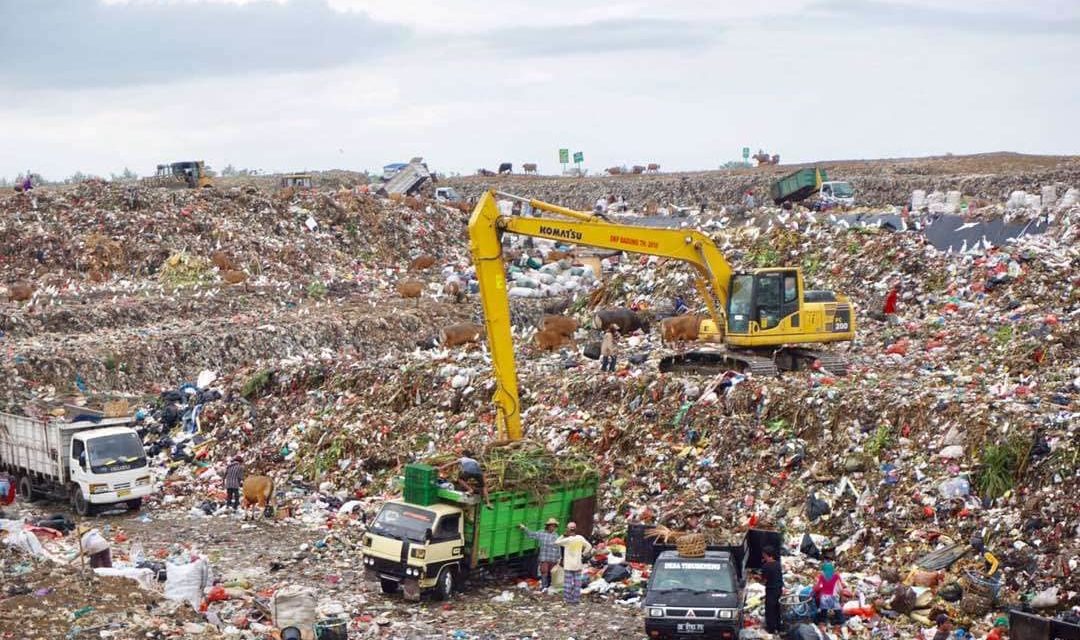

This Waste releases methane gas which immediately reacts with oxygen and changes its condition. Why did this happen?
If not managed properly, waste which generally comes from organic waste which is “anthropogenic waste” will degrade and decompose into methane gas (CH 4 ). CH 4 gas is a greenhouse gas that can cause a greenhouse effect which has the potential to cause global warming.
Refrigerator and air conditioner
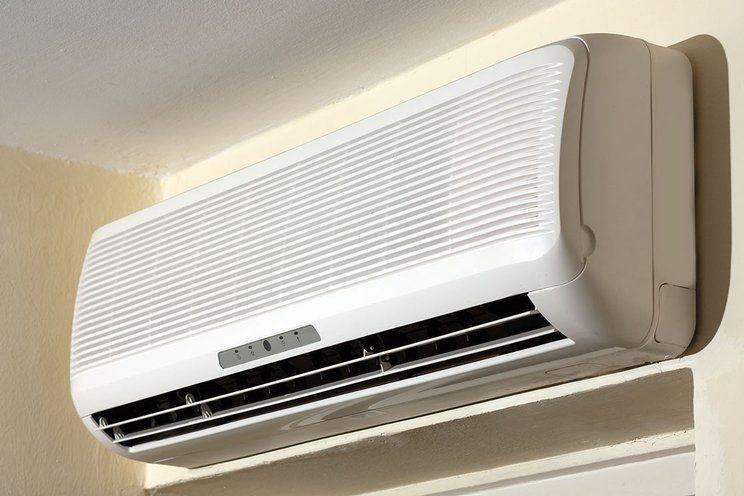

Refrigerators and air conditioners are used in almost every home and office. These tools use Freon gas or CFC (Cloro Fouro Carbon).
Freon can deplete the ozone layer when it is put into the air and is one of the causes of global warming. This ozone layer is useful for protecting the earth and living things from exposure to Ultra Violet B (UV-B) radiation and also absorbs high ultraviolet radiation from the sun from reaching the earth.
Fossil Burning
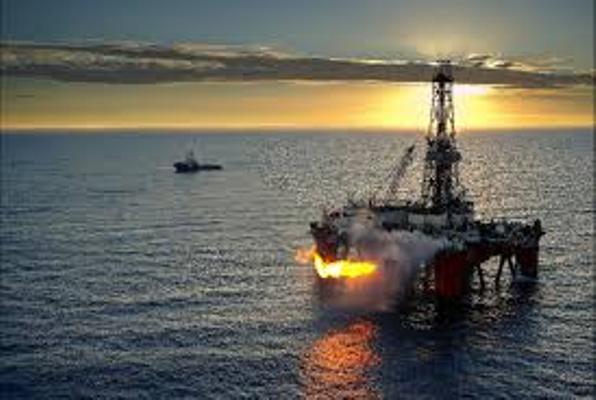

Fossil fuels include gas, oil and coal. The main producer of CO₂ is Australia which has been widely recognized for many years compared to others. When fossil fuels are burning, carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere.
The cause of this pollution in Australia has been linked to electricity where around 73% of electricity comes from burning coal and about 14% from burning gas. The remaining 13% comes from sources such as wind, sun and water or water. In fact, less pollution is achieved when the amount of gas, coal, several sources of energy. The burning of fossil fuels has for years been recognized as the main cause of global warming.