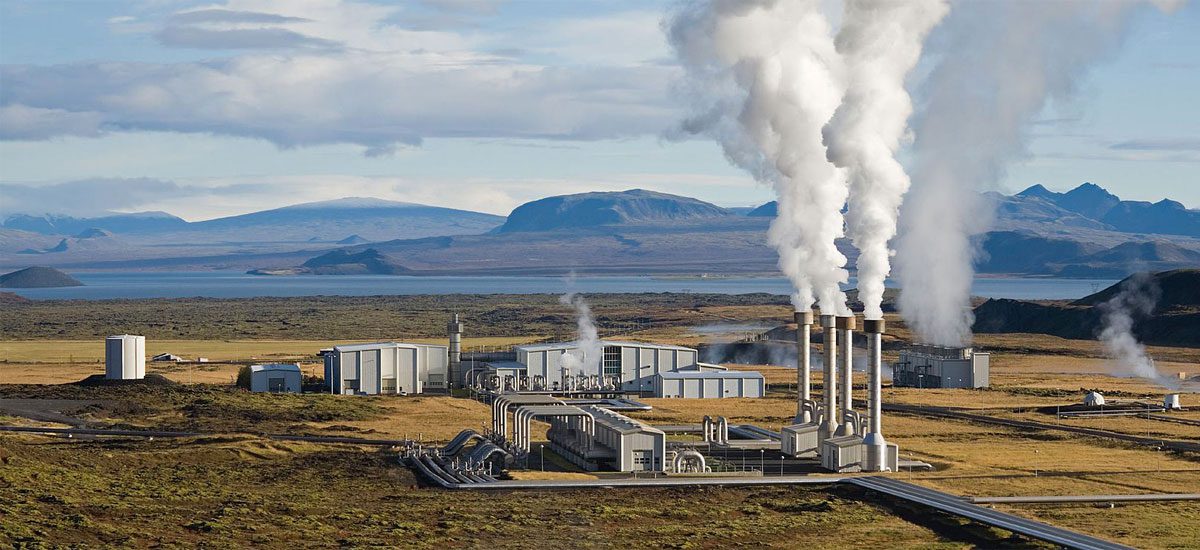
Things that need attention in choosing technology for using geothermal energy to be converted into electrical energy are:
- Temperature; geothermal fluids with a high temperature of> 225 oC have long been used for electricity generation. Medium temperature 150 – 225 oC
- Resource reserves of up to 25-30 years
- Steam Quality; It is expected that the pH is almost neutral, because if the pH is very low the corrosion rate of the material will be faster.
- Well Depth and Chemical Content Usually not very deep (no more than 3 km). The location is relatively easy to reach.
- The likelihood of a hydrothermal eruption is relatively low. The production of hot fluid from the bowels of the earth can increase the risk of hydrothermal eruptions.
Geological Characteristics of Geothermal Areas
- Heat Source: Magma which has a temperature of ~ 700 C
- Bed Rock: The bedrock layer which is the hard rock of the lower layer
- Aquifer (Permeable Zone Layer): is a layer that can be flowed by water. This layer serves as a reservoir
- Cap Rock: A layer of hard rock as a cover rock layer.
- Water Replishment: as water enhancer.
- Surface Manifestation, namely: Symptoms that appear on the earth’s surface (craters, hot springs, geysers, volcanoes, etc.).
Benefits of Geothermal Energy
How Geothermal Power Plants Work
How does Geothermal Power Plant work?
For more details on how the PLTP works, let’s look at the picture and description below.
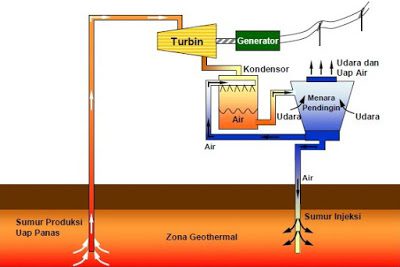
1. Steam is supplied from production wells through a steam transmission system which then enters the Steam Receiving Header as a steam collecting medium. The Steam Receiving Header is equipped with a Rupture Disc which functions as the last safety unit. If there is over pressure in the Steam Receiving, the steam will be discharged through the Vent Structure. The Vent Structure functions for warming-up in the pipe line when starting the unit and as a safety valve that will relieve pressure if a sudden trip occurs.
2. From the Steam Receiving Header, the steam is then flowed to a Separator (Cyclone Type) which functions to separate steam (pure steam) from foreign objects such as heavy particles (Sodium, Potassium, Calcium, Silica, Boron, Ammonia, Fluor etc.).
3. Then the steam enters the Demister which functions to separate the moisture contained in the steam, so it is hoped that clean steam will enter the turbine.
4. The steam enters the turbine so that the energy conversion occurs from the heat energy contained in the steam into kinetic energy which is received by the turbine blades. The turbine which is coupled with the generator will cause the generator to rotate when the turbine rotates so that there is a conversion from kinetic energy to mechanical energy.
5. The rotating generator produces Electricity
6. Exhaust Steam from the Turbine is condensed in the Condenser with a Jet Spray system (Direct Contact Condensor).
7. NCG (Non Condensable Gas) which enters the Condenser is sucked by the First Ejector then enters the Intercondensor as a cooling medium and NCG catcher. After from the Intercondensor, NCG is sucked again by the Second Ejector into the Aftercondensor as a cooling medium and then discharged into the atmosphere through the Cooling Tower.
8. From the condenser, the water from the condensation is flowed by the Main Cooling Water Pump into the Cooling Tower. Furthermore, the cooling water from the cooling tower, dry steam, is recirculated back into the condenser as a cooling medium.
9. The Primary Cooling System besides being a cooler the Secondary Cooling System also fills the cooling water to the Intercondensor and Aftercondensor.
10. The overflow from the Cold Basin Cooling Tower will be accommodated for the benefit of the Reinjection Pump.
11. River Make-Up Pump operates only when filling the Basin Cooling Tower.
Advantages And Disadvantages of Geothermal Power Plants
Advantage
