Now we will discuss a laboratory tool that is no less familiar, namely the laboratory desiccator.
The topics that we will discuss in this article include the definition of a desiccator, the function of a desiccator, how to use a desiccator and the price of a laboratory desiccator. Here’s the review:
what is desiccator
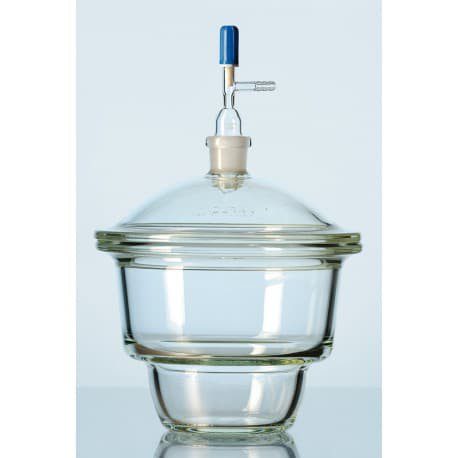
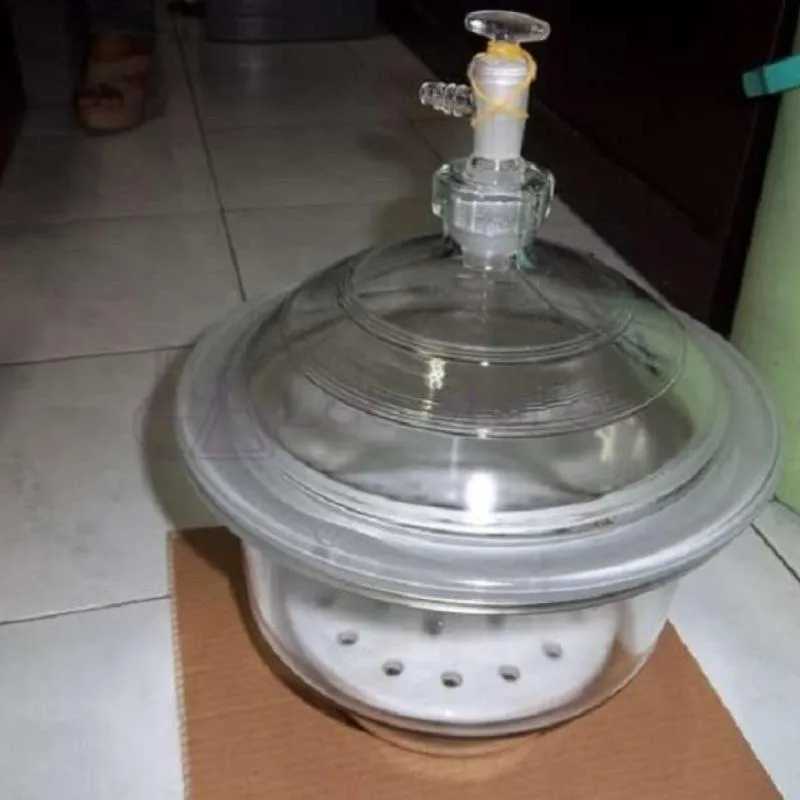
A desiccator is a laboratory instrument made of glass or glass. The desiccator usually has a shape that is almost similar to the food jar in our homes.
This tool is composed of a container, cover and silica gel. The lid of the desiccator usually has a hole that is very useful in drying the sample in it.
Desicator Function
A desiccator functions to remove water content in a test sample. It can also be used to remove crystals in the test sample.
A desiccator is often used in the analysis of water content testing with the help of silica gel in it. This silica gel functions as a vaporizer that can bind the water present in the sample.

Desicator Working Principle
The principle or method of working of a desiccator is to bind the water content in the sample. Silica gel will bind H2O before the sample completely loses its water content.
The test sample is put in a desiccator and has moisture because the water will be bound by the silica gel in it. The silica gel will then experience a color change which indicates that the water is bound.
If the silica has changed color, it is best to dry the silica in an oven at 105 degrees Celsius or replace it with new silica if necessary.
Kinds of Desiccators
Just like other laboratory equipment, it turns out that there are 2 different types of desiccators, namely:
- Ordinary Desiccator : Ordinary desiccator is a desiccator that only consists of a container, cover and silica gel.
- Vacuum desiccator : Unlike the usual desiccator, the vacuum desiccator consists of an additional vacuum device. The vacuum in this desiccator is useful for sucking all the water content in the sample.
Conclusion
After reading the article above, there are several points that we can draw conclusions about this desiccator, namely:
- A desiccator is a container made of glass and is impermeable to air in it.
- A desiccator is a laboratory tool that functions to dry test samples with the help of silica gel.
- Silica gel in the desiccator serves to bind the water content in the sample.
That is the meaning and function of a laboratory desiccator. Hopefully this article is useful for those of you who are looking for a reference about the desiccator and its function as a laboratory tool.