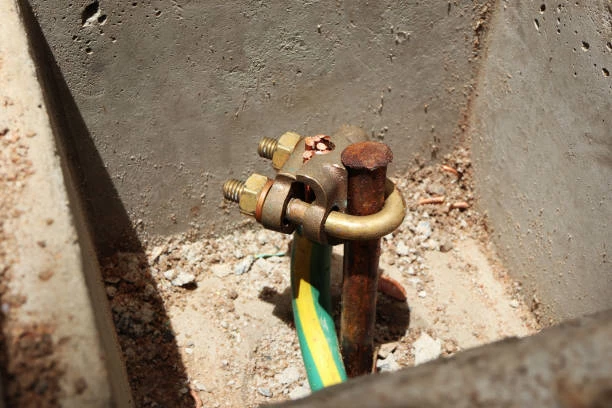
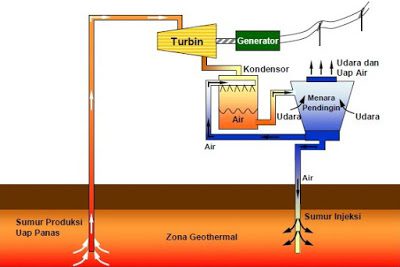
As we know, this ground is also known as grounding. Where this grounding or grounding is a complementary system that is in every electrical installation. Its own function is as a grounding system.
In addition, the installation of grounding is also useful to provide protection for home electrical installations from various disturbances and hazards. How, interested to know more about Arde?
In this article, we will thoroughly discuss what is a grounding or grounding system. Starting from the understanding, function, how it works, symbols, to how to install and how to make a simple ground. We will also examine whether grounding can save electricity.
Definition of Electrical Grounding
When viewed from its function, it can be said that grounding or what is also known as grounding is a grounding system in the form of a separate cable line that does not connect with other electrical wiring installations installed in home electrical installations to the ground point (earth) .
So this system was created with the aim of eliminating the potential difference that occurs in the electrical circuit . In addition, at the same time aims to release the excess electric charge that arises.
With the installation of grounding, when there is an excess load on the electrical installation, the charge will automatically flow into the ground.
Because the soil has a very large mass and volume, if there are disturbances or problems related to electric charge, it will be quickly neutralized. It is for this purpose that a grounding or grounding system is installed.
Electrical Grounding / Grounding Function
Judging from its function, of course this Ground or Grounding needs to be installed in every electrical installation, right? Whether it’s for personal needs such as home areas or industrial areas such as factories, of course it requires the presence of Ground as security.
The function of grounding is as a form of protection. By installing grounding, electrical installations can avoid the following risks:
- Grounding serves to prevent large electrical leakage. For example, in the event of an electric short circuit, insulation leakage, and avoiding people from being exposed to electric shocks.
- Prevents in the event of an induction in the flow voltage.
- Serves as a protector from the threat of static electricity. Especially static electricity that has a voltage with a very high scale such as a lightning strike.
- Grounding also serves as a reference for measuring the electric current in the installation.
- Grounding can also prevent damage caused by voltage leakage.
- Ground also serves to neutralize noise caused by several factors. Among them due to the quality of components that are far from standard or power quality that is not good.
How Electric Ground Works
If observed, the ground installation area is generally deliberately placed close to the kWh meter. So from the kWh meter, the neutral and ground cables are combined together with the phase cable. Then this cable will be connected to the entire network and also the socket.
From this socket, the grounding will be connected and connected to various electrical equipment . For example, home electrical appliances such as refrigerators, TVs, radios, computers and so on.
Grounding symbol
In general, grounding or ground is denoted by certain symbols. This electrical installation symbol is used when you want to draw an electronic circuit .
Let’s take a look at some of the most common Ground symbols below. Use the following symbols to explain what the meaning of Grounding is each.

Various Grounding Systems
When making electrical installations, of course the security system is the most important thing to pay attention to. Therefore, carrying out a grounding or grounding system is important to do.
Before discussing further about how to install a grounding cable, of course we need to know the various types. The following is a discussion of various grounding systems that you need to know.
1. Safety Grounding
Safety grounding is one system that is often used in grounding installations. Safety grounding is used with the aim of neutralizing the impact of dangerous electric currents.
For example, if there is a voltage and electric current that goes up or down. Whether it’s caused by an electromagnetic wave whose source of emission comes from a flash of lightning or comes from various other reasons.
To overcome this, the installation of safety grounding can be an option. Because of this, safety grounding systems are often applied to various electrical lines. It is easy to say that grounding is one of the lightning protection systems.
2. RF Grounding
RF grounding is a grounding system whose designation is generally used in communication devices. One example is like radio. As for the process of installing RF grounding , it is mostly applied to devices with large needs.
The purpose of the installation of this system is to reduce the impact of radiation. Especially to ward off the risk of radiation. As we know, this radiation can arise from the emission of radio communication waves.
Wire Color For Ground

Before you install a grounding system, of course you also need to know the standard size of the home electrical installation cable. Because this cable is the main component needed to make ground or grounding.
The wire for grounding is usually green or yellow with a green stripe. Cables with yellow green are generally used for conductors.
For example, its use for various types of conductors. For example, such as earthing conductors and protective conductors. In addition, this yellow green wire is also used to connect equipotential bonds to the ground.
Cable Size For Ground
The ground wire for the grounding system is done by planting a pipe in the ground. Where this pipe will be installed on the terminal part of the socket.
How to install the grounding on the socket must meet the applicable size standards so that its function can be maximized.
What you need to know, too, is that the installation method will affect the level of security and also the quality of the ground.
Therefore, the size and specifications of the cable are also points that should not be ruled out if you want to install grounding at home, right?
The size of the house electrical cable for grounding can later be adjusted to the standards that have been set. The following is the standard size of the power cord for installing grounding in areas of the house that need attention.
- The use of wires for grounding generally uses yellow-green wires.
- Minimum grounding cable diameter using a 50 mm cross-section. But when using a cable with a larger diameter is also allowed.
- Especially for grounding or grounding in a location that is quite sensitive, try using the HVSC (High Voltage Single Core) cable.
- For outdoor installations, grounding can use a 50 mm NYA type cable.
How to Install a Good and Standardized Ground
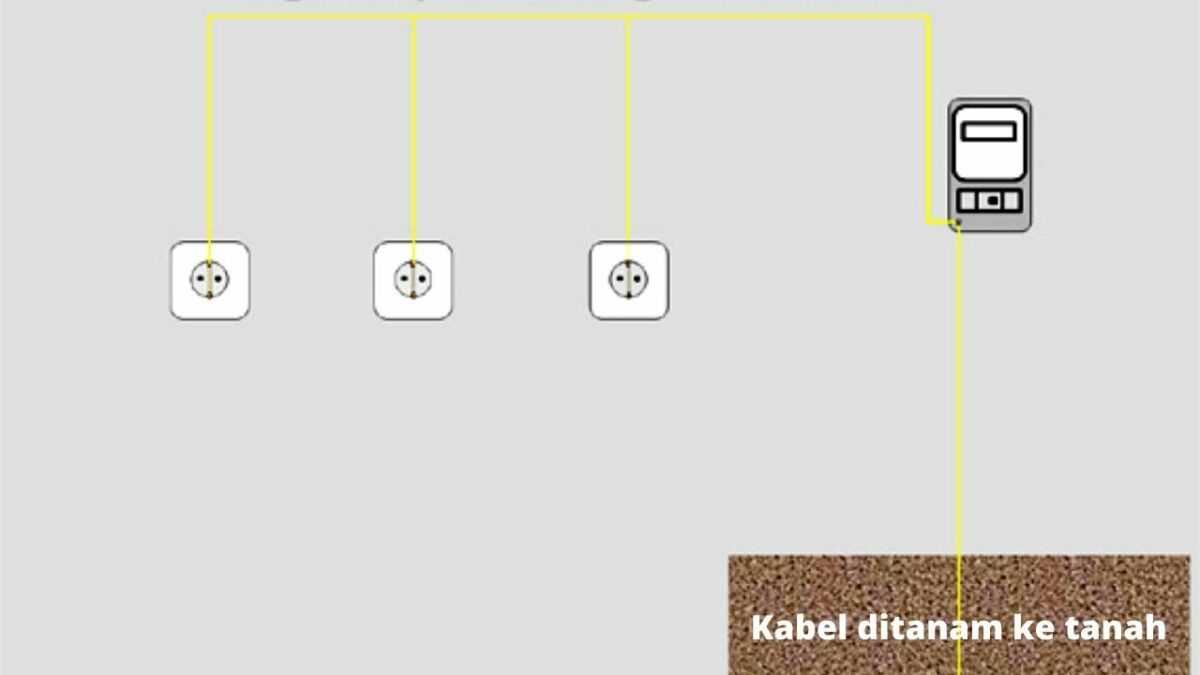
The size of the power cord and its strength do have different specifications. The larger the diameter used for grounding, the better the flow of electric current in the circuit.
With a good flow of electric current, it will not cause a greater burden. In addition, the waste of electricity can also be avoided. So, if someone asks whether grounding can save electricity?
So the answer is yes. Logically, this grounding or grounding will make the flow of electricity in each circuit better than before. How, of course interesting if you can save electricity, right? In addition, the security of the installation is also more guaranteed with this Grounding.
Let’s just look at how to install a good grounding cable and of course according to the standards below:
1. Installing the Grounding Rod
Installing a grounding or grounding rod is an important step that should not be missed. The more ground rods installed, the better for the installation.
What are the requirements for installing a grounding rod? Here are the steps that need to be done.
- Ground rods should be planted with more than one number. Also, make sure to be at least 5 meters apart from each other.
- Ground rods should be installed more than one and arranged in parallel.
- Ground rods should be avoided from sandy or rocky soil types because they are poor media.
- To maximize the grounding system, stick rods should be planted at a distance not too far from the house.
2. Material Selection For Ground
To install a good grounding, the material used is also very important to note.
What are the points to consider when choosing a material for grounding?
- Choosing a cable that complies with standards is very important. Both in terms of size, color, and type and material.
- For stick rods, choose ones made of solid copper.
- Because iron is a material that rusts easily and is not durable. We recommend that the use of iron material for grounding can be avoided.
3. Planting Grounding Rod
The way to install the grounding cable is the next stage, namely the process of planting the grounding rod. You will of course need to dig at the location to be grounded or grounded.
The electrical grounding depth should not be less than 50 cm from the ground level. More fully, here are some steps that you need to do.
- First of all, dig a hole with a vertical position and with a depth of approximately 50 cm.
- After that, plug the stick rod into the hole firmly.
- Pour enough water into the dug hole. It can also be filled with water until the hole is full.
- Press the rod down, then lift it for a while so that the water can enter and seep into the soil.
- Next, re-insert the stick rod to the desired depth.
4. Connecting the Earth to the Cable
After installing the grounding rod, the next step is to ground the wire. For the process of connecting the ground to the wire, it will be easier if you use the exothermic welding method.
This exothermic method is carried out by mixing copper material that has previously been melted at high temperatures. Then the copper liquid can be used to permanently join the conductors.
After the welding is complete, you can clean the surface to be joined from dirt. The goal is to make the connection stronger and not easily separated.
5. Planting Cable Arde
The steps for installing the last ground are by planting a ground wire. For this one method, you can apply the following methods:
- Before embedding the ground wire, you can first measure the grounding resistance. For this purpose, you can take advantage of special tools such as an ohm meter or a grounding tester.
- After that, dig the soil to the predetermined grounding points.
- Excavate the track to the grounding terminal with a depth of 40 cm to 50 cm.
- Next, pull the cable through the path. Make sure the size of the power cord used is of sufficient length.
- After all the connections are connected, put the marking pipe in that place as a marker.
- Next, fill the soil with a minimum height of 20 cm.
- Put a mark on the excavation as a marker that the place has been grounded.
The Right way to install Ground
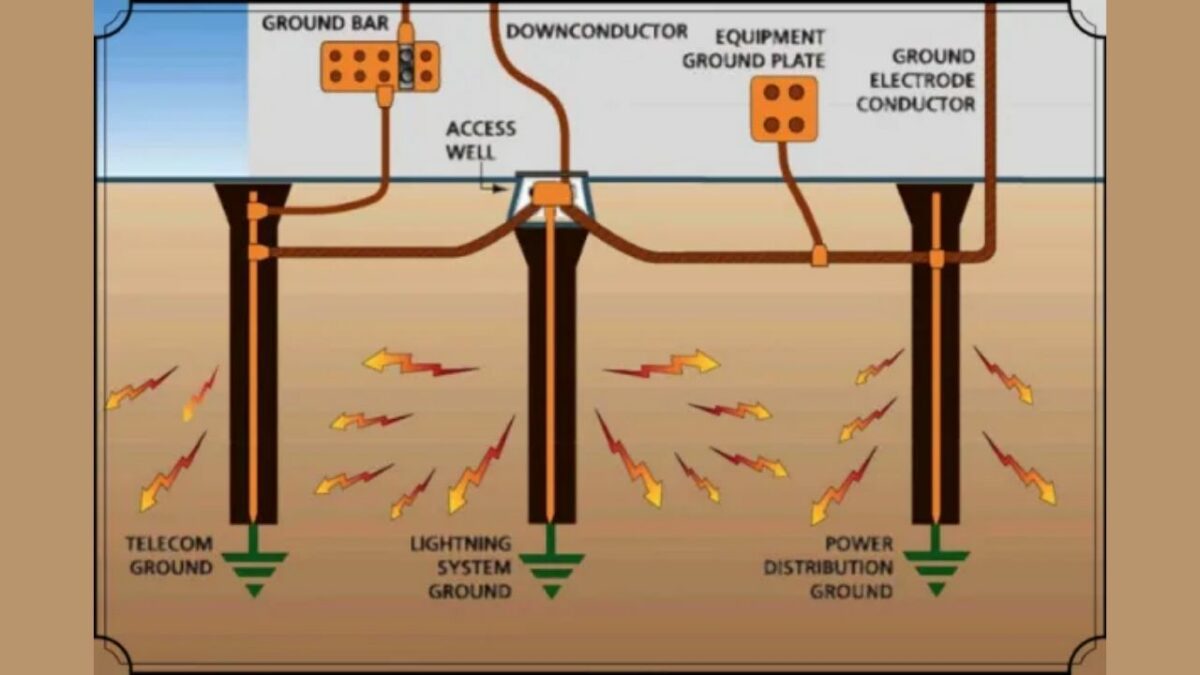
In order for the grounding installation to function optimally, of course you must follow good and correct installation standards.
What needs to be considered when installing grounding? Here is the full review.
- Provide a pipe with a minimum size of 75 cm
- Planting pipes for grounding should be avoided from places that allow the emergence of puddles when it rains.
- The distance for the ground pipe and also the kWh meter box should not be too close. For example, in a group with a minimum distance of 180 cm to avoid the kWh meter from being struck by lightning when bad weather occurs.
- The cross-sectional area of the grounding should be expanded and the conducting depth deepened.
- The system for new grounding should be made with a parallel system .
Conclusion
Grounding or grounding is a grounding system that is often installed in various electrical installations. The main purpose of this grounding is as a means of protecting electrical installations from various problems and disturbances. One of them is from an electric short circuit, lightning strike when it rains and other risks.
Then, can grounding save electricity? The installation of grounding can also save electricity consumption. With the grounding system, the electrical voltage can be neutralized so that the load is not too much.
This also affects the obstacles that arise to be reduced. So that automatically the use of electric power will be reduced. So, do you understand the function of grounding in electrical installations?